Kubernetes Cluster Connector Settings Reference
This topic provides settings and permissions for the Kubernetes Cluster Connector.
The Kubernetes Cluster Connector is a platform-agnostic connection to a Kubernetes cluster located anywhere.
For cloud platform-specific connections, see platform Cloud Connectors.
Looking for the How-to? See Add a Kubernetes Cluster Connector.
Video Summary
Here's a 10min video that walks you through adding a Harness Kubernetes Cluster Connector and Harness Kubernetes Delegate. The Delegate is added to the target cluster and then the Kubernetes Cluster Connector uses the Delegate to connect to the cluster:
Kubernetes Cluster Connector vs Platform Connectors
The Kubernetes Cluster Connector is platform-agnostic. Use it to access a cluster on any platform.
It cannot also access platform-specific services and resources. For those, use a platform Connector like Google Cloud Platform or Amazon Web Services.
See Add a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Connector, Add an AWS Connector.
For example, let's say you have a GKE Kubernetes cluster hosted in Google Cloud Platform (GCP). You can use the Kubernetes Cluster Connector to connect Harness to the cluster in GCP. The Kubernetes Cluster Connector cannot also access Google Container Registry (GCR).
In this case, you have two options:
- Use a Google Cloud Platform Connector to access the GKE cluster and all other GCP resources you need.
- Set up a Kubernetes Cluster Connector for the GKE cluster. Next, set up a Google Cloud Platform Connector for all other GCP services and resources.
When you set up a deployment in Harness, you will specify Connector to use for the artifact and target cluster. If we use option 2 above, you will select a Google Cloud Platform Connector for the GCR container. Next, you will select Kubernetes Cluster Connector for the target cluster.
Which option you choose will depend on how your teams use Harness.
Permissions Required
The IAM roles and policies needed by the account used in the Connector depend on what operations you are using with Harness and what operations you want Harness to perform in the cluster.
You can use different methods for authenticating with the Kubernetes cluster, but all of them use a Kubernetes Role.
The Role used must have either the cluster-admin permission in the target cluster or admin permissions in the target namespace.
For a detailed list of roles and policies, see Harness Role-Based Access Control Overview.
Harness CI Permission Requirements
If you are only using the Kubernetes Cluster Connector for Harness Continuous Integration (CI), you can use a reduced set of permissions.
For Harness CI, the Delegate requires CRUD permissions on Secret and Pod.
Here is a same Service Account and RoleBinding that lists the minimum permissions:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: cie-test
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: cie-test-sa
namespace: cie-test
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: sa-role
namespace: cie-test
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["list", "watch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: sa-role-binding
namespace: cie-test
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cie-test-sa
namespace: cie-test
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: sa-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Builds (CI)
A Kubernetes service account with CRUD permissions on Secret, Service, Pod, and PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC).
For more information, see User-Facing Roles from Kubernetes.
Deployments (CD)
A Kubernetes service account with permission to create entities in the target namespace is required. The set of permissions should include list, get, create, watch (to fetch the pod events), and delete permissions for each of the entity types Harness uses. In general, cluster admin permission or namespace admin permission is sufficient.
If you don’t want to use resources: [“*”] for the Role, you can list out the resources you want to grant. Harness needs configMap, secret, event, deployment, and pod at a minimum for deployments, as stated above. Beyond that, it depends on the resources you are deploying via Harness.
If you don’t want to use verbs: [“*”] for the Role, you can list out all of the verbs (create, delete, get, list, patch, update, watch).
The YAML provided for the Harness Delegate defaults to cluster-admin because that ensures anything could be applied. Any restriction must take into account the actual manifests to be deployed.
Harness CI Cluster Requirements
For Harness Continuous Integration, the resources required for the Kubernetes cluster depends on the number of builds running in parallel, as well as the resources required for each build.
Below is a rough estimation of the resources required, based on the number of daily builds:
| PRs/Day | Nodes with 4 CPU, 8GB RAM,100GB disk | Nodes with 8 CPU, 16GB RAM, 200GB disk |
| 100 | 19 - 26 | 11 - 15 |
| 500 | 87 - 121 | 45 - 62 |
| 1000 | 172 - 239 | 89 - 123 |
Credential Validation
When you click Submit, Harness uses the provided credentials to list controllers in the default namespace in order to validate the credentials. If validation fails, Harness does not save the Connector and the Submit fails.
If your cluster does not have a default namespace, or your credentials do not have permission in the default namespace, then you can check Skip default namespace validation to skip this check and saving your Connector settings.
You do not need to come back and uncheck Skip default namespace validation.
Later, when you define a target Infrastructure using this Connector, you will also specify a specific namespace. During deployment, Harness uses this namespace rather than the default namespace.
When Harness saves the Infrastructure it performs validation even if Skip default namespace validation was checked.
Name
The unique name for this Connector.
ID
See Entity Identifier Reference.
Description
Text string.
Tags
See Tags Reference.
Cluster Details
Manual or Use a Delegate
Recommended: Install and run the Harness Kubernetes Delegate in the target Kubernetes cluster, and then use the Kubernetes Cluster Connector to connect to that cluster using the Harness Kubernetes Delegate you installed. This is the easiest method to connect to a Kubernetes cluster.You can select to enter the authentication details of the target cluster or use the role associated with a Harness Delegate.
When you select a Delegate, the Harness Delegate will inherit the Kubernetes service account associated with the Delegate pod.
The service account associated with the Delegate pod must have the Kubernetes cluster-admin role.
See Install a Kubernetes Delegate.
Master URL
The Kubernetes master node URL. The easiest method to obtain the master URL is using kubectl:
kubectl cluster-info
Authentication
Select an authentication method.
Basic (Username and Password) authentication is not recommended. Basic authentication has been removed in GKE 1.19 and later.
Username and Password
Username and password for the Kubernetes cluster. For example, admin or john@example.com, and a Basic authentication password.
You can use an inline username or a Harness Encrypted Text secret.
For the password, select or create a new Harness Encrypted Text secret.
This is not used, typically. Some Connectors have Basic authentication disabled by default. The cluster would need Basic authentication enabled and a specific username and password configured for authentication.For OpenShift or any other platform, this is not the username/password for the platform. It is the username/password for the cluster.
Service Account
Add the service account token for the service account. The token must be pasted in decoded in the Encrypted Text secret you create/select.
To get a list of the service accounts, run kubectl get serviceAccounts.
For example, here's a manifest that creates a new SA named harness-service-account in the default namespace.
# harness-service-account.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: harness-service-account
namespace: default
Next, you apply the SA.
kubectl apply -f harness-service-account.yml
Next, grant the SA the cluster-admin permission (see Permissions Required above).
# harness-clusterrolebinding.yml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: harness-admin
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: harness-service-account
namespace: default
Next, apply the ClusterRoleBinding.
kubectl apply -f harness-clusterrolebinding.yml
Once you have the SA added, you can gets its token using the following commands.
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME={SA name}
NAMESPACE={target namespace}
SECRET_NAME=$(kubectl get sa "${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -o=jsonpath='{.secrets[].name}')
TOKEN=$(kubectl get secret "${SECRET_NAME}" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -o=jsonpath='{.data.token}' | base64 -d)
echo $TOKEN
The | base64 -d piping decodes the token. You can now enter it into the Connector.
OpenID Connect
These settings come from the OIDC provider authorization server you have set up and others come from the provider app you are using to log in with.
First let's look at the authorization server-related settings:
Master URL
The issuer URI for the provider authentication server.
For example, in Okta, this is the Issuer URL for the Authorization Server:
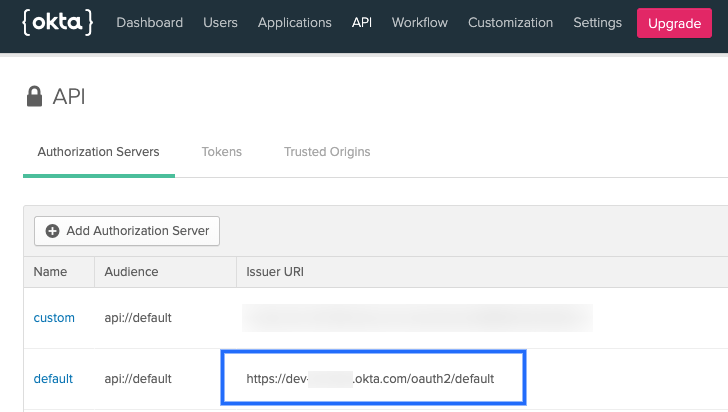 (./static/kubernetes-cluster-connector-settings-reference-02.png)
Providers use different API versions. If you want to identify the version also, you can obtain it from the token endpoint.
(./static/kubernetes-cluster-connector-settings-reference-02.png)
Providers use different API versions. If you want to identify the version also, you can obtain it from the token endpoint.
In Okta, in the authentication server Settings, click the Metadata URI. Locate the token_endpoint. Use the token_endpoint URL except for the /token part. For example, you would use https://dev-00000.okta.com/oauth2/default/v1 from the following endpoint:
"token_endpoint":"https://dev-00000.okta.com/oauth2/default/v1/token"
OIDC Username and Password
Login credentials for a user assigned to the provider app.
- OIDC Client ID: Public identifier for the client that is required for all OAuth flows. In Okta, this is located in the Client Credentials for the app:
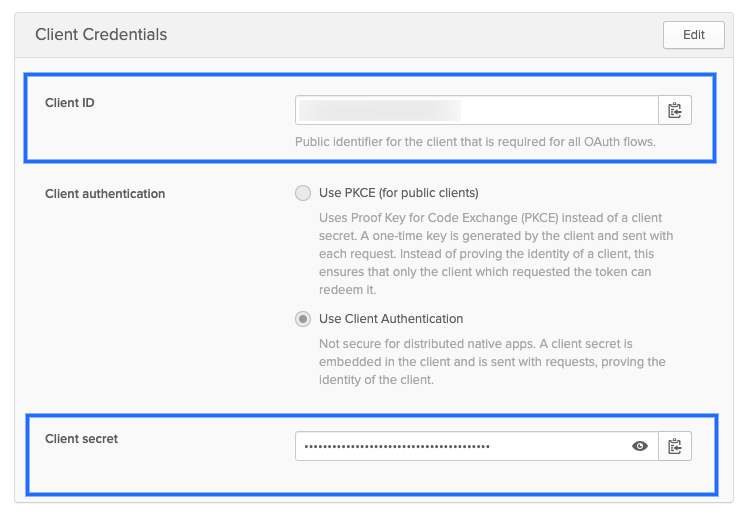 (./static/kubernetes-cluster-connector-settings-reference-04.png)
(./static/kubernetes-cluster-connector-settings-reference-04.png)
OIDC Secret
The client secret for the app. For Okta, you can see this in the above picture.
OIDC Scopes
OIDC scopes are used by an application during authentication to authorize access to a user's details, like name and picture. In Okta, you can find them in the Authorization Server Scopes tab:
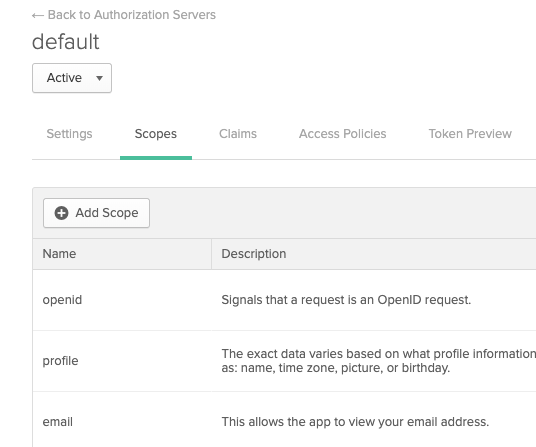 (./static/kubernetes-cluster-connector-settings-reference-06.png)
If you enter multiple scopes, separate them using spaces.
(./static/kubernetes-cluster-connector-settings-reference-06.png)
If you enter multiple scopes, separate them using spaces.
The remaining OIDC Token settings are part of the provider app you are using to log in.
Client Key Certificate
Client Key
Create or select a Harness secret to add the client key for the client certificate. The key can be pasted into the secret either Base64 encoded or decoded.
Client Key passphrase
Create or select a Harness secret to add the client key passphrase. The passphrase can be pasted in either Base64 encoded or decoded.
Client Certificate
Create or select a Harness secret to add the client certificate for the cluster.
The public client certificate is generated along with the private client key used to authenticate. The certificate can be pasted in either Base64 encoded or decoded.
Client Key Algorithm (optional)
Specify the encryption algorithm used when the certificate was created. Typically, RSA.
CA Certificate (optional)
Create or select a Harness secret to add the Certificate authority root certificate used to validate client certificates presented to the API server. For more information, see Authenticating from Kubernetes.
Amazon AWS EKS Support
AWS EKS is supported using the Inherit Delegate Credentials option in the Kubernetes Cluster Connector settings. You can use your EKS service account token as well.
To install a delegate in your AWS infrastructure, do the following:
- Install a Harness Kubernetes Delegate in your EKS cluster.You must be logged in as an admin user when you run the
kubectl apply -f harness-delegate.yamlcommand. - Give it a name that you can recognize as an EKS cluster Delegate. For information on installing a Kubernetes Delegate, see Install a Kubernetes Delegate.
- In the Kubernetes Cluster Connector settings, select the Delegate.
- When setting up the EKS cluster as the target Infrastructure, select the Kubernetes Cluster Connector.
OpenShift Support
This section describes how to support OpenShift using a Delegate running externally to the Kubernetes cluster. Harness does support running Delegates internally for OpenShift 3.11 or greater, but the cluster must be configured to allow images to run as root inside the container in order to write to the filesystem.Typically, OpenShift is supported through an external Delegate installation (shell script installation of the Delegate outside of the Kubernetes cluster) and a service account token, entered in the Service Account setting.
You only need to use the Master URL and Service Account Token setting in the Kubernetes Cluster Connector settings.
The following shell script is a quick method for obtaining the service account token. Run this script wherever you run kubectl to access the cluster.
Set the SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME and NAMESPACE values to the values in your infrastructure.
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME=default
NAMESPACE=mynamepace
SECRET_NAME=$(kubectl get sa "${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -o json | jq -r '.secrets[].name')
TOKEN=$(kubectl get secret "${SECRET_NAME}" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -o json | jq -r '.data["token"]' | base64 -D)
echo $TOKEN
Once configured, OpenShift is used by Harness as a typical Kubernetes cluster.
OpenShift Notes
- If you decide to use a username/password for credentials in the Harness Kubernetes Cluster Connector, do not use the username/password for the OpenShift platform. Use the username/password for the cluster.
- Harness supports DeploymentConfig, Route, and ImageStream across Canary, Blue Green, and Rolling deployment strategies. Please use
apiVersion: apps.openshift.io/v1and notapiVersion: v1. - The token does not need to have global read permissions. The token can be scoped to the namespace.
- The Kubernetes containers must be OpenShift-compatible containers. If you are already using OpenShift, then this is already configured. But be aware that OpenShift cannot simply deploy any Kubernetes container. You can get OpenShift images from the following public repos: https://hub.docker.com/u/openshift and https://access.redhat.com/containers.
- Useful articles for setting up a local OpenShift cluster for testing: How To Setup Local OpenShift Origin (OKD) Cluster on CentOS 7, OpenShift Console redirects to 127.0.0.1.
YAML Example
connector:
name: Doc Kubernetes Cluster
identifier: Doc_Kubernetes_Cluster
description: ""
orgIdentifier: ""
projectIdentifier: ""
tags: {}
type: K8sCluster
spec:
credential:
type: ManualConfig
spec:
masterUrl: https://00.00.00.000
auth:
type: UsernamePassword
spec:
username: john.doe@example.io
passwordRef: account.gcpexample