Built-in and custom Harness variables reference
This topic describes the default (built-in) and custom Harness expressions, as well as the prefixes used to identify user-created variables. This list will be periodically updated when new expressions are added to Harness.
Looking for how-tos? See Variable Expressions How-tos.
Variable expression basics
Let's quickly review what Harness built-in and custom variable expressions are and how they work.
What is a Harness variable expression?
Harness variables are a way to refer to something in Harness, such as an entity name or a configuration setting. At pipeline runtime, Harness evaluates all variables and replaces them with the resulting value.
Harness variables are powerful because they let you template configuration information, pipeline settings, and values in your scripts, and they enable your pipelines to pass information between stages and settings.
When you use a variable, you add it as an expression.
Harness expressions are identified using the <+...> syntax. For example, <+pipeline.name> references the name of the pipeline where the expression is evaluated.
The content between the <+...> delimiters is passed on to the Java Expression Language (JEXL) where it is evaluated. Using JEXL, you can build complex variable expressions that use JEXL methods. For example, here is an expression that uses Webhook Trigger payload information:
<+trigger.payload.pull_request.diff_url>.contains("triggerNgDemo") || <+trigger.payload.repository.owner.name> == "wings-software"
Harness pre-populates many variables, as documented below, and you can set your own variables in the form of context output from shell scripts and other steps.
You can use all Java string methods
You can use all Java string methods on Harness variable expressions.
The above example used contains():
<+trigger.payload.pull_request.diff_url>.contains("triggerNgDemo")
Let's look at another example. Imagine you have a variable called abc with the value def:ghi. You can use split() like this:
echo <+pipeline.variables.abc.split(':')[1]>
The result would be ghi.
FQNs and expressions
Everything in Harness can be referenced by a Fully Qualified Name (FQN) expression.
The FQN is the path to a setting in the YAML of your pipeline.
You can select the expression for a setting or value in the pipeline editor or execution.
You don't need to build the expression yourself. Harness provides multiple places where you can copy the variable expression.
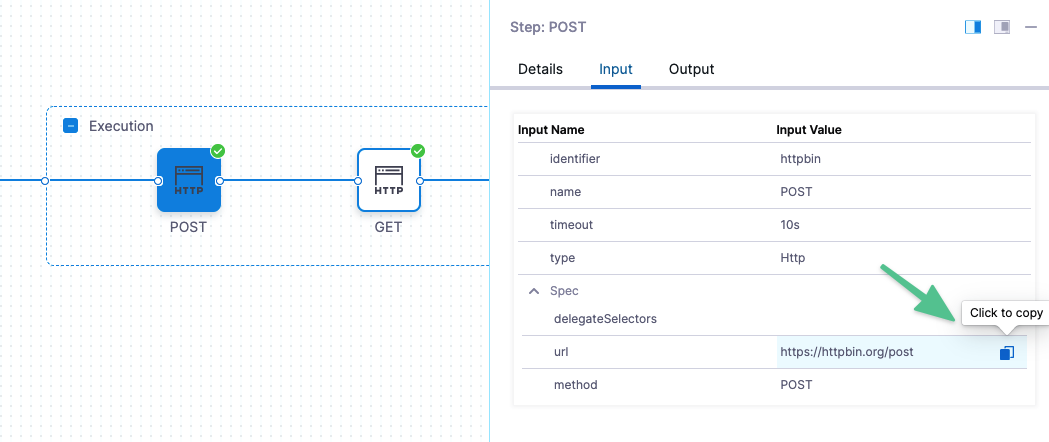
For example, you can click the copy button in a pipeline execution to get the expressions of settings and values.
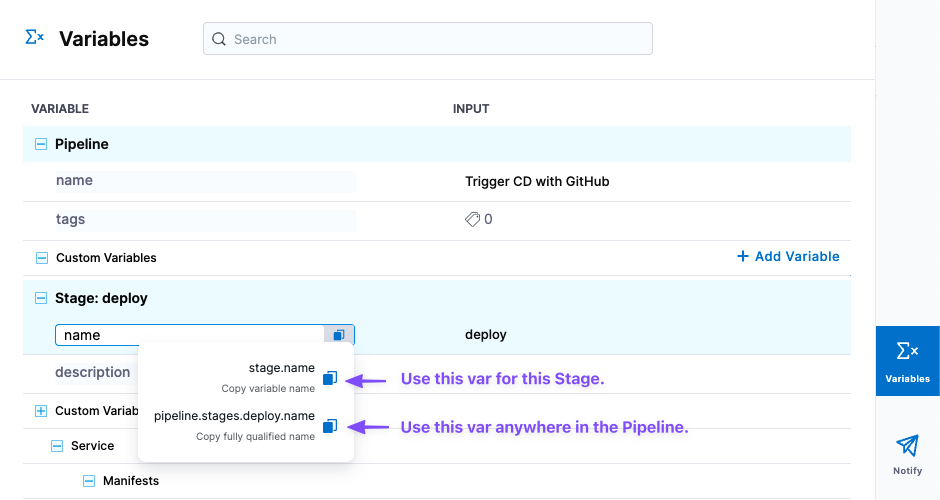
When building a pipeline in pipeline studio, you can copy the FQN of a setting using Variables.
Stage level and pipeline level expressions
Every section and step in a stage contains input information you can reference as expressions.
Click Variables in the pipeline to view all the inputs and copy their expressions.
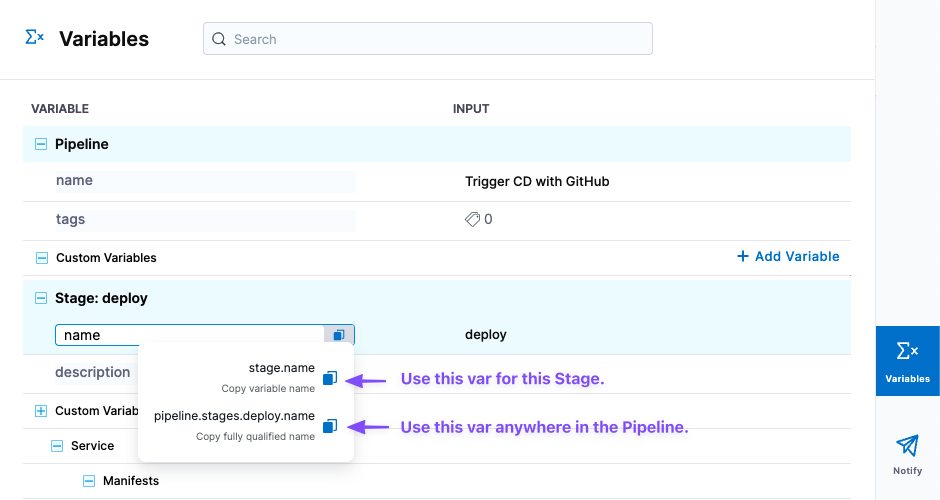
There are two expressions for each input:
- Stage-level: Use this option to reference the input anywhere in its stage.
- Pipeline-level: Begins with
pipeline.stages. Use this option to reference the input anywhere in the pipeline.
Expression example
Here is a simple example of a Shell script step echoing some common variable expressions.
echo "Harness account name: "<+account.name>
echo "Harness comp name: "<+account.companyName>
echo "pipeline executionId: "<+pipeline.executionId>
echo "pipeline sequenceId: "<+pipeline.sequenceId>
echo "stage name: "<+stage.name>
echo "service name: "<+service.name>
echo "service variables: "<+serviceVariables.example_var>
echo "artifact image: "<+artifacts.primary.image>
echo "artifact image path: "<+artifacts.primary.imagePath>
echo "environment name: "<+env.name>
echo "infrastructure connectorRef: "<+infra.connectorRef>
echo "infrastructure namespace: "<+infra.namespace>
echo "infrastructure releaseName: "<+infra.releaseName>
Here is an example of the output.
Harness account name: Harness.io
Harness comp name: Harness.io
pipeline executionId: T4a7uBs7T-qWhNTr-LnFDw
pipeline sequenceId: 16
stage name: dev
service name: nginx
service variables: foo
artifact image: index.docker.io/library/nginx:stable
artifact image path: library/nginx
environment name: quickstart
infrastructure connectorRef: account.harnesstestpmdemocluster
infrastructure namespace: default
infrastructure releaseName: docs
Command completed with ExitCode (0)
Input and output variable expressions
You can reference the inputs and outputs of any part of your pipeline.
- Input variable expressions reference the values and setting selections you made in your pipeline.
- Output variable expressions reference the results of a pipeline execution.
You can reference inputs in pipeline Variables.
Input and output variable expressions in executions
Inputs and outputs are displayed for every part of the pipeline execution.
Here are the inputs and outputs for a Kubernetes rollout deployment step.
| Inputs | Outputs |
|---|---|
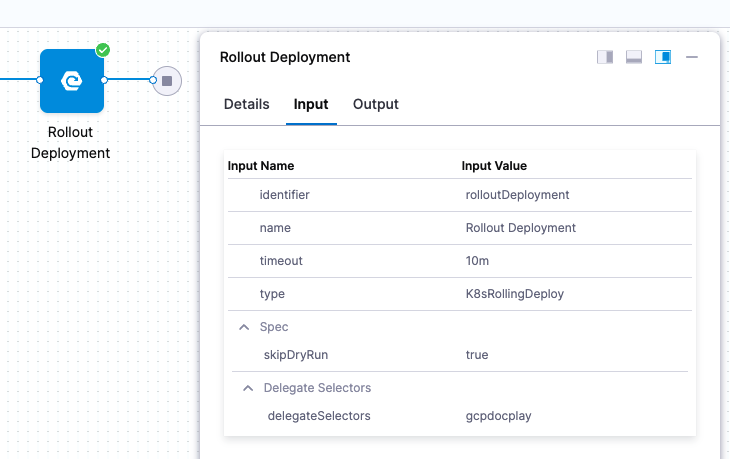 | 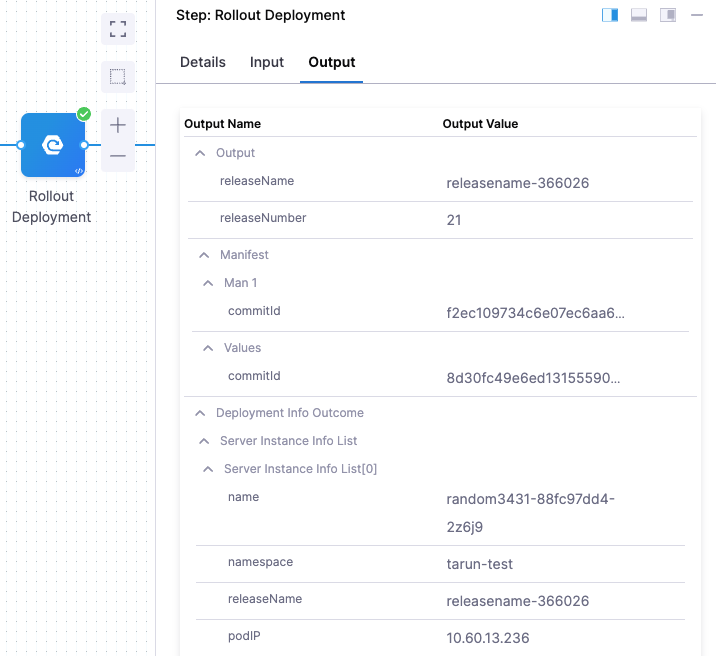 |
You can copy the expressions for the names or values of any input or output.
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
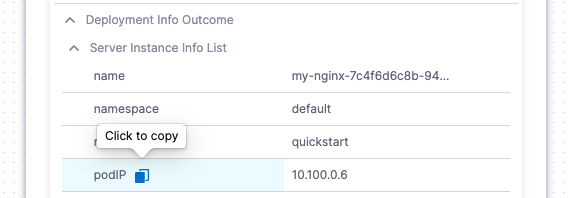 | 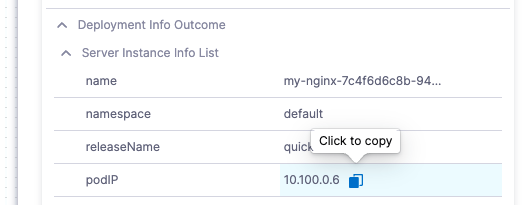 |
Here are the Name and Value expressions for the podIP setting.
- Name:
<+pipeline.stages.Deploy_Service.spec.execution.steps.rolloutDeployment.deploymentInfoOutcome.serverInstanceInfoList[0].podIP>
- Value:
10.100.0.6
Using expressions in settings
You can use Harness variable expressions in most settings.
When you select Expression in a setting, you type <+ and a value and the list of available variables appears.
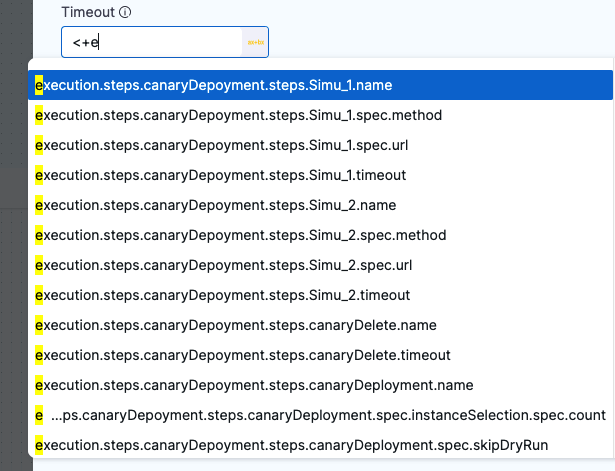
Simply click a variable expression name to use it as the value for this setting.
At runtime, Harness will replace the variable with the runtime value.
You can also paste expressions that don't appear. For example, expressions that reference settings in previous stages.
See Fixed Values, Runtime Inputs, and Expressions.
Only use expressions after they ll be resolved
When Harness encounters an expression during pipeline execution, it tries to resolve the expression with the information it has at that point in the execution. Consequently, you can use an expression only after Harness has the required information. If you try to use an expression before Harness has its information, it will fail.
In this illustration, you can see how the information in each section of the stage is referenced.
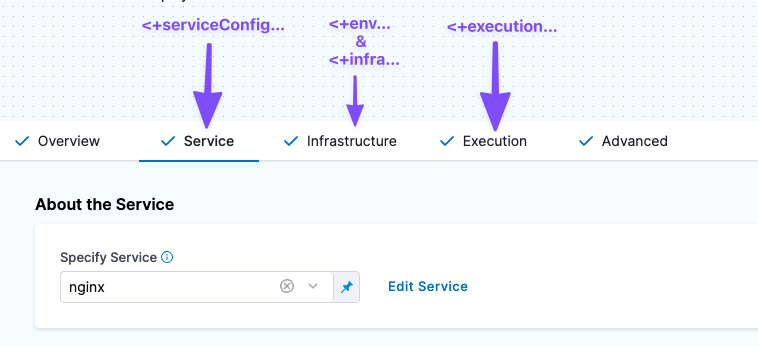
Here is how you reference the information in each of these sections.
- Service expressions can only be used after Harness has progressed through the Service section of the pipeline.
- Service expressions they can be used in Infrastructure and Execution.
- Infrastructure expressions can only be used after Harness has progressed through the Infrastructure section of the pipeline.
- In Infrastructure, you can reference Service settings.
- Since Execution follows Infrastructure, you can reference Infrastructure expressions in Execution.
- Execution expressions apply to steps in Execution.
- Each step's Execution expressions can only be used after Harness has progressed through that step in the Execution section:
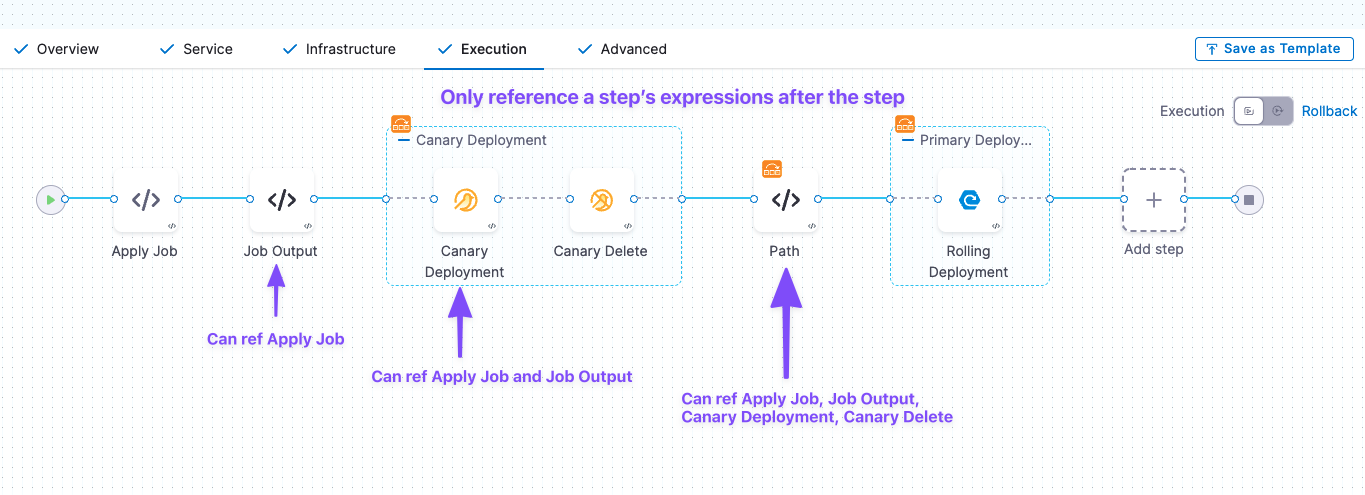
- Each step's Execution expressions can only be used after Harness has progressed through that step in the Execution section:
Variable expressions in conditional execution settings
Stages and steps support variable expressions in the JEXL conditions of their Conditional Execution settings.
You can only use variable expressions in the JEXL conditions that can be resolved before the stage.
Since Conditional Execution settings are used to determine if the stage should be run, you cannot use variable expressions that can't be resolved until the stage is run.
For more information on conditional execution, go to Stage and Step Conditional Execution Settings.
Variable expression limitations and restrictions
Review the following variable expression limitations and restrictions to avoid errors when using variable expressions.
Scope
Harness permits variables only within their scope. You will not see a variable available in a field where it cannot be used.
You cannot refer to a pipeline step's expressions within the same step.
For example, if you have an HTTP step with the Id foo you cannot use the expression <+execution.steps.foo.spec.url> to reference the HTTP URL within that same step. Put another way, you can only reference a step's settings from a different step.
Variable value size
A variable value (the evaluated expression) is limited to 256 KB.
Harness expressions not allowed in comments of Values YAML or Kustomize patches
You cannot use Harness expressions in comments in:
- Values YAML files (values.yaml) in Kubernetes, Helm chart, or Native Helm deployments.
- Kustomize patches files.
For example, here is a values.yaml file with a Harness expression in the comment:
name: test
replicas: 4
image: <+artifacts.primary.image>
dockercfg: <+artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret>
createNamespace: true
namespace: <+infra.namespace>
# using expression <+infra.namespace>
This values.yaml file will not process successfully. Remove any expressions from comments and the file will process successfully.
Scripts within expressions
You cannot write scripts within an expression <+...>. For example, the following script will not work.
if ((x * 2) == 5) { <+pipeline.name = abc>; } else { <+pipeline.name = def>; }
Variable names across the pipeline
Variables names must be unique within the same stage. You can use same variable names in different stages of the same pipeline or other pipelines.
Hyphens in variable names
Do not use hyphens (dashes) in variable names, as some Linux distributions and deployment-related software do not allow them. Also, it can cause issues with headers.
For example, <+execution.steps.httpstep.spec.headers.x-auth> will not work.
As a workaround, you can put the variable name in ["..."]. For example, <+execution.steps.httpstep.spec.headers["x-auth"]>
This also works for nested expressions. For example:
<+execution.steps.httpstep.spec.newHeaders["x-auth"]["nested-hyphen-key"]>
<+execution.steps.httpstep.spec.newHeaders["x-auth"].nonhyphenkey>
Variable expression name restrictions
A variable name is the name in the variable expression, such as foo in <+stage.variables.foo>.
Variable names may only contain a-z, A-Z, 0-9, _. They cannot contain hyphens or dots.
Certain platforms and orchestration tools, like Kubernetes, have their own naming restrictions. For example, Kubernetes doesn't allow underscores. Ensure that whatever expressions you use resolve to the allowed values of your target platforms.
Reserved words
The following keywords are reserved, and cannot be used as a variable name or property.
or and eq ne lt gt le ge div mod not null true false new var return shellScriptProvisioner
See JEXL grammar details.
Number variables
Number type variables are always treated as doubles (double-precision floating-point).
- -1.79769313486231E308 to -4.94065645841247E-324 for negative values
- 4.94065645841247E-324 to 1.79769313486232E308 for positive values
For example, here is a pipeline variable of number type.
variables:
- name: double_example
type: Number
description: ""
value: 10.1
The expression to reference that pipeline variable, <+pipeline.variables.double_example>, will be treated as a double when it is resolved to 10.1.
Numbers as doubles and strings
Whether the number in a variable is treated as a double or string depends on the field that you use it in.
If you enter 123 in a string filed, such as a name, it is treated as a string. If you enter 123 in a count field, such as instance count, it is treated as a double.
Contains
When using contains, ensure the expression is wrapped within <+ > and the specific string is within ".
For example, <+stage.name.contains("s1")>.
Split
When using split, ensure the expression is wrapped within <+ >.
For example, <+pipeline.variables.abc.split(':')[1]>.
Complex expression
When using a complex expression, ensure the expression is wrapped within <+ >.
For example, <+ <+trigger.payload.pull_request.diff_url.contains("triggerNgDemo")> || <+trigger.payload.repository.owner.name> == "wings-software">.
Ternary operators
When using ternary conditional ?: operators, do not use spaces between the operators and values. Ensure the expression is wrapped within <+ >.
For example, <+condition ? <value_if_true> : <value_if_false>> will not work. Use <+condition?<value_if_true>:<value_if_false>> instead.
Equals
When using == condition, ensure the expression is wrapped within <+ >.
For example, <+<+pipeline.name> == "pipeline1"> or <+<+stage.variables.v1> == "dev">.
Variable concatenation
Harness recommends that you use Java string method for concatenating pipeline variables. Ensure the expression is wrapped within <+ >.
For example, use syntax <+pipeline.variables.var1.concat("_suffix")> or <+<+pipeline.variables.var1>.concat("_suffix")> or <+<+pipeline.variables.var1> + "_suffix"> instead of <+pipeline.variable.var1>_suffix.
Forward references
Harness does not support referencing variables from future steps. For example, in a pipeline with four steps: step A, B, C and D, you cannot reference variables from step C in step A.
You can reference the variable, <+env.name> (environment name) in a service step.
Built-in CIE codebase variables reference
In Harness, you set up your codebase by connecting to a Git repo using a Harness connector and cloning the code you wish to build and test in your pipeline.
Harness also retrieves your Git details and presents them in your build stage once a pipeline is run.
Using Harness built-in expressions, you can refer to the various attributes of your codebase in Harness stages.
Here is a simple example of a Shell script step echoing some common codebase variable expressions.
echo <+codebase.commitSha>
echo <+codebase.targetBranch>
echo <+codebase.sourceBranch>
echo <+codebase.prNumber>
echo <+codebase.prTitle>
echo <+codebase.commitRef>
echo <+codebase.repoUrl>
echo <+codebase.gitUserId>
echo <+codebase.gitUserEmail>
echo <+codebase.gitUser>
echo <+codebase.gitUserAvatar>
echo <+codebase.pullRequestLink>
echo <+codebase.pullRequestBody>
echo <+codebase.state>
See Built-in CIE Codebase Variables Reference.
Account
<+account.identifier>
The entity identifier of the Harness account.
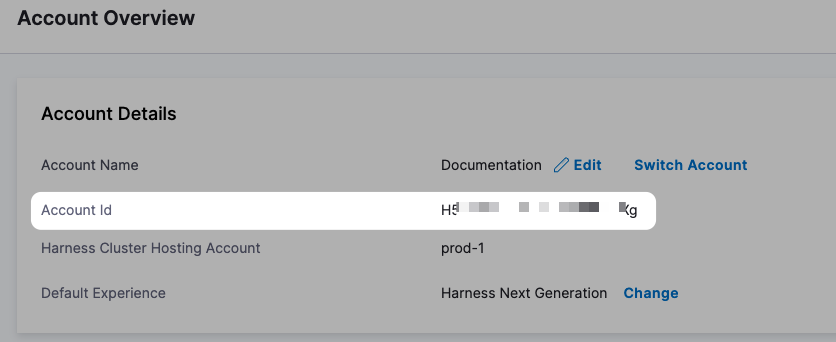
<+account.name>
Harness account name.
<+account.companyName>
The name of the company for the account.
Custom account variables
See Add Account, Org, and Project-level Variables.
Org
<+org.identifier>
The entity identifier of an organization.
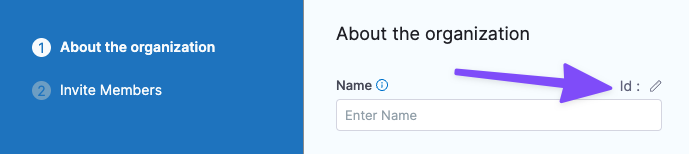
<+org.name>
The name of the org.
<+org.description>
The description of the org.
Custom org variables
See Add Account, Org, and Project-level Variables.
Project
<+project.name>
The name of the Harness project.
<+project.description>
The description of the Harness project.
<+project.tags>
All Harness Tags attached to the project.
<+project.identifier>
The entity identifier of the Harness project.
Custom project variables
See Add Account, Org, and Project-level Variables.
Pipeline
Pipeline-level variables
Here is a quick video that explains how to create and reference pipeline, stage, and service variables.
<+pipeline.identifier>
The Entity Identifier (Id) for the pipeline.
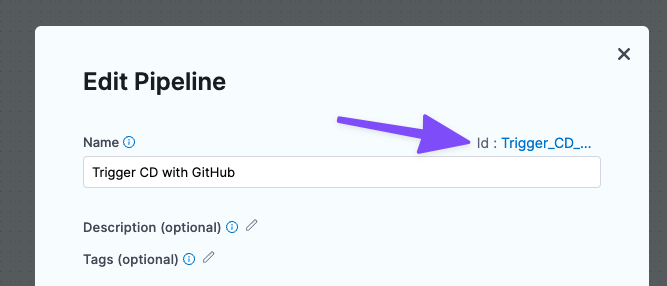
<+pipeline.executionId>
Every execution of a pipeline is given a universally unique identifier (UUID). The UUID can be referenced anywhere.
For example, in the following execution URL, the UUID follows executions and is kNHtmOaLTu66f_QNU-wdDw.
https://app.harness.io/ng/#/account/12345678910/cd/orgs/default/projects/CD_Quickstart/pipelines/Helm_Quickstart/executions/kNHtmOaLTu66f_QNU-wdDw/pipeline
<+pipeline.executionUrl>
The execution URL of the pipeline. This is the same URL you see in your browser when you are viewing the pipeline execution.
For example:
https://app.harness.io/ng/#/account/12345678910/cd/orgs/default/projects/CD_Docs/pipelines/Triggers/executions/EpE_zuNVQn2FXjhIkyFQ_w/pipeline
The expression <+pipeline.execution.Url> has been deprecated.
<+pipeline.name>
The name of the current pipeline.
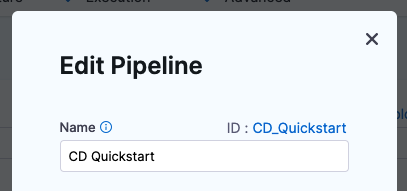
<+pipeline.sequenceId>
The incremental sequential ID for the execution of a pipeline. A <+pipeline.executionId> does not change, but a <+pipeline.sequenceId> is incremented with each run of the pipeline.
The first run of a pipeline receives a sequence ID of 1 and each subsequent execution is incremented by 1.
For CD pipelines, the ID is named execution. For CI pipelines, the ID is named builds.
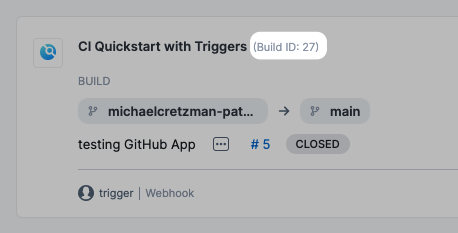
You can use <+pipeline.sequenceId> to tag a CI build when you push it to a repo, and then use <+pipeline.sequenceId> to pull the same build and tag in a subsequent stage. For an example, go to the Build and test on a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure tutorial.
<+pipeline.startTs>
The start time of a pipeline execution in Unix Epoch format. See Trigger How-tos.
<+pipeline.triggerType>
The type of trigger. See Trigger How-tos.
Here are the possible <+pipeline.triggerType> and <+trigger.type> values.
| <+pipeline.triggerType> | <+trigger.type> | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ARTIFACT | Artifact | New artifact trigger. For example, new Docker Hub image tag |
| SCHEDULER_CRON | Scheduled | Scheduled Cron trigger |
| MANUAL | null | Pipeline triggered using the RUN button in the user interface |
| WEBHOOK_CUSTOM | Custom | Custom webhook trigger |
| WEBHOOK | Webhook | SCM webhook trigger. For example, GitHub pull request |
<+pipeline.triggeredBy.name>
The name of the user or the trigger name if the pipeline is triggered using a webhook. See Trigger Pipelines using Git Events.
If a user name is not present in the event payload, the <+pipeline.triggeredBy.name> expression will resolve as empty. For example, in the SaaS edition of Bitbucket, a user name is not present.
<+pipeline.triggeredBy.email>
The email of the user who triggered the pipeline. This returns NULL if the pipeline is triggered using a webhook. See Trigger How-tos.
<+pipeline.selectedStages>
The list of stages selected for execution.
<+pipeline.delegateSelectors>
The pipeline level delegate selectors selected via runtime input.
Deployment and step status
Deployment status values are a Java enum. The list of values can be seen in the deployments Status filter:
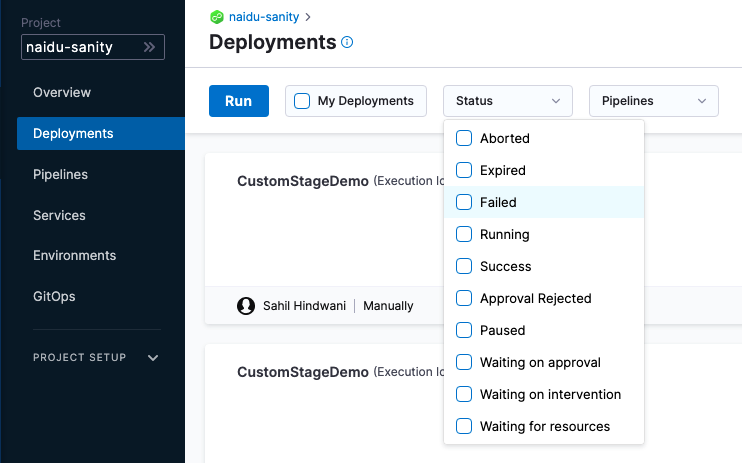
You can use any status value in a JEXL condition. For example, <+pipeline.stages.stage1.status> == "FAILED".
Step status
The expression <+pipeline.stages.[stage name].spec.execution.steps.[step Id].status> resolves to the status of a step. For example, <+pipeline.stages.MyStageName.spec.execution.steps.mystep.status>.
You must use the expression after the step in execution.
InputSet
Input Set values are a Json value. The list of values can be searched via
<+inputSet>
Stage
Stage-level variables
Here is a quick video that explains how to create and reference pipeline, stage, and service variables.
Once you've created a stage, its settings are in the Overview tab. For example, here is the Overview tab for a deploy stage.
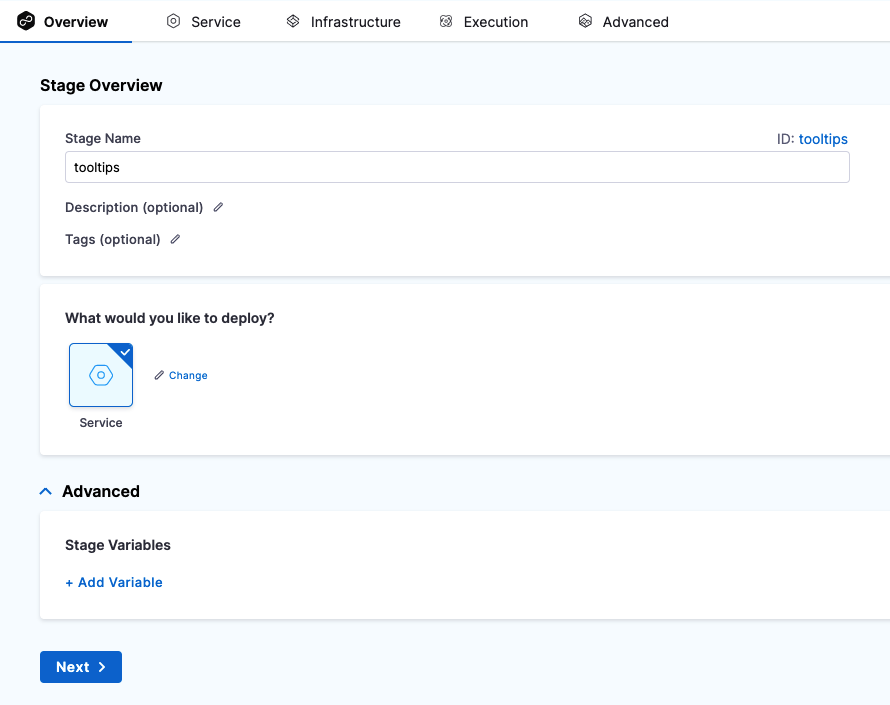
In Advanced, you can add Stage Variables.
Stage variables are custom variables you can add and reference in your stage and pipeline. They're available across the pipeline. You can override their values in later stages.
You can even reference stage variables in the files fetched at runtime.
For example, you could create a stage variable name and then reference its identifier in the Kubernetes values.yaml file used by this stage: name: <+stage.variables.name>:
name: <+stage.variables.name>
replicas: 2
image: <+artifacts.primary.image>
...
When you run this pipeline, the value for name is used for the values.yaml file. The value can be a fixed value, expression, or runtime input.
You reference stage variables within their stage using the expression <+stage.variables.[variable name]>.
You reference stage variables outside their stage using the expression <+pipeline.stages.[stage name].variables.[variable name]>.
<+stage.name>
The name of the stage where the expression is evaluated.
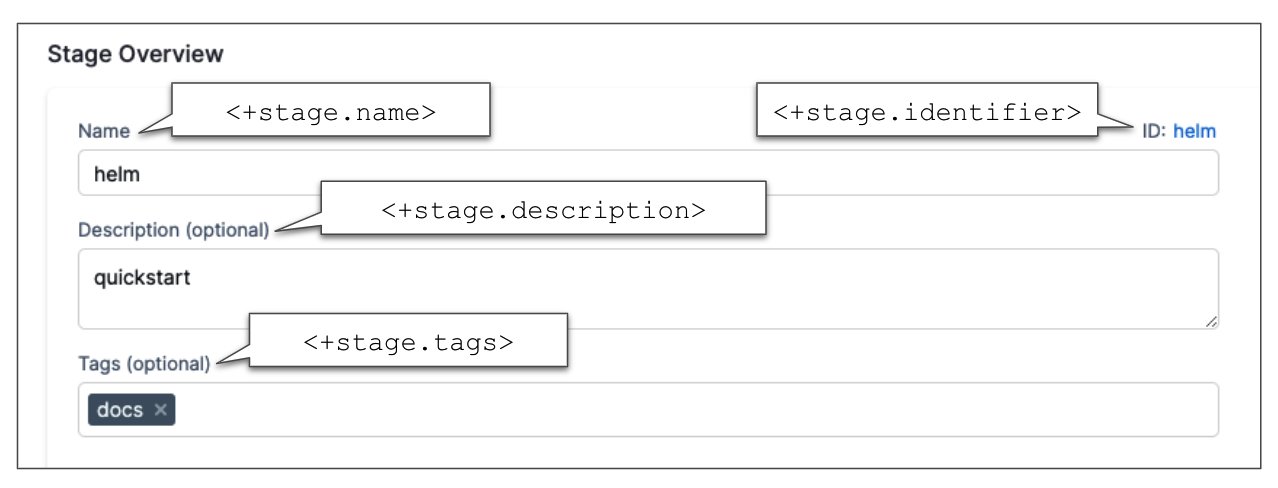
<+stage.description>
The description of the stage where the expression is evaluated.
<+stage.tags>
The tags on the stage where the expression is evaluated. See Tags Reference.
These tags are different from Docker image tags.
<+stage.identifier>
The entity identifier of the stage where the expression is evaluated.
<+stage.output.hosts>
Lists all of the target hosts when deploying to multiple hosts.
When you are deploying to multiple hosts, such as with an SSH, WinRM, or deployment template stage, you can run the same step on all of the target hosts.
To run the step on all hosts, you use the repeat Looping Strategy and identify all the hosts for the stage as the target.
repeat:
items: <+stage.output.hosts>
Here is an example with a Shell script step.
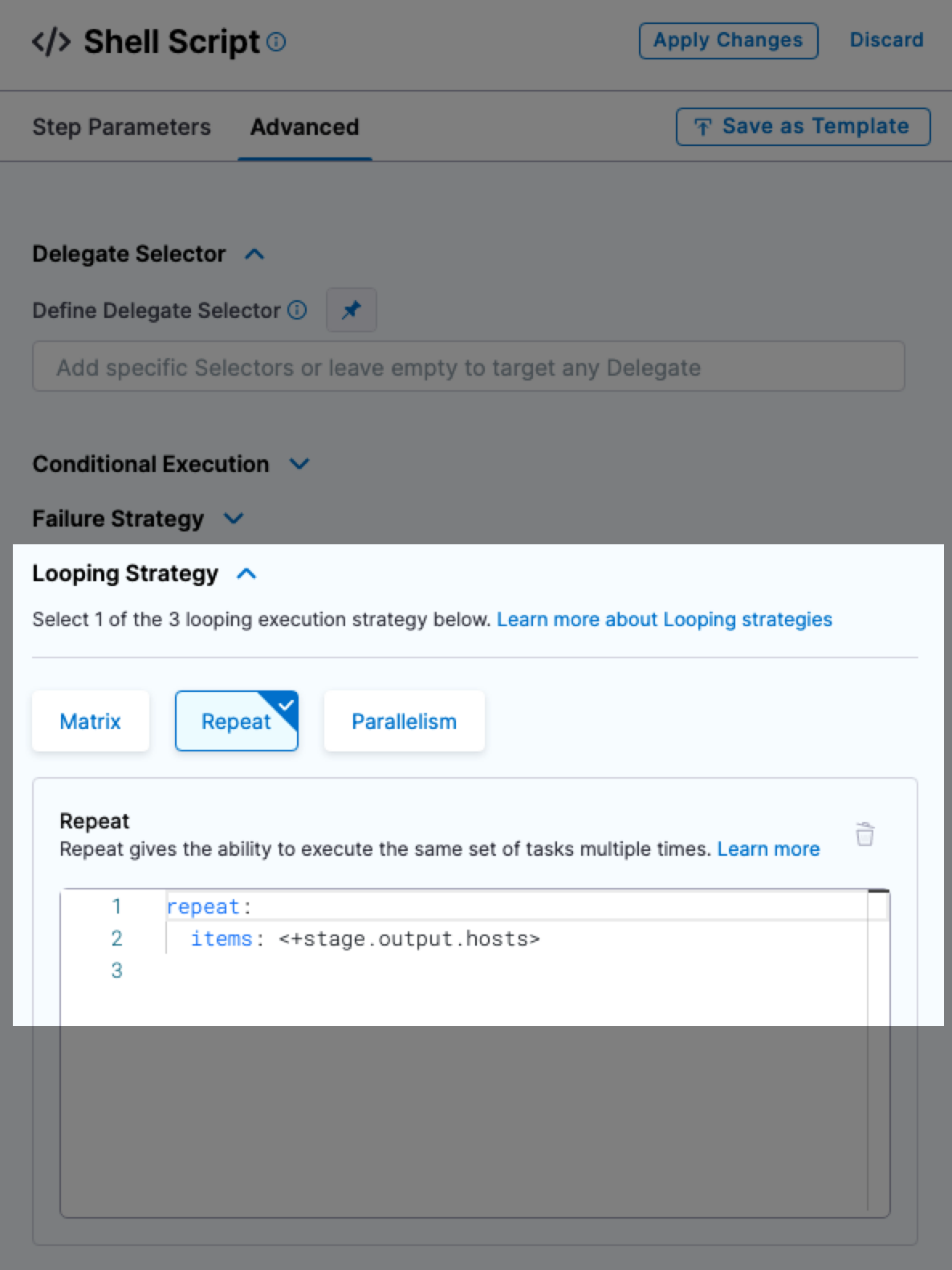
For examples, see the looping strategies used in the Secure Shell (SSH) deployment tutorial.
<+stage.executionUrl>
The execution URL of the stage. This is the same URL you see in your browser when you are viewing the pipeline execution.
Use the following fully qualified expression to get the execution URL for a specific stage in the pipeline:
<+pipeline.stages.[stageId].executionUrl>
<+stage.delegateSelectors>
The stage level delegate selectors selected via runtime input
Service
Currently, there are two versions of services and environments, v1 and v2. Services and environments v1 are being replaced by services and environments v2.
The use of variable expressions is different between v1 and v2.
For more information, go to Services and Environments Overview.
Service-level variables for service v2
To reference a service variable, use the expression <+serviceVariables.[variable name]>.
For example, <+serviceVariables.myvar>.
Service-level variables for service v1
Here is a quick video that explains how to create and reference pipeline, stage, and service variables.
<+serviceConfig.serviceDefinition.spec.variables.[var_name]>
The value of the service-level variable in [var_name].
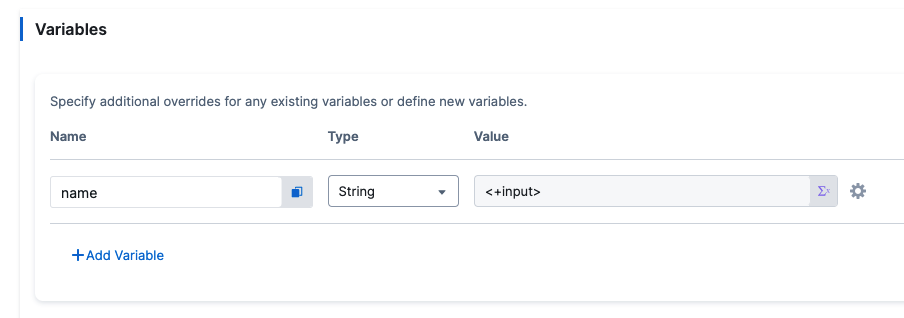
Use expression anywhere after the service step in the pipeline.
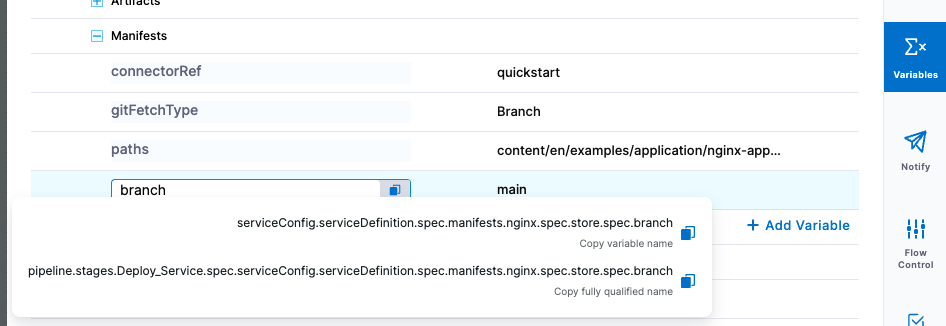
To reference the variables, click the copy button.
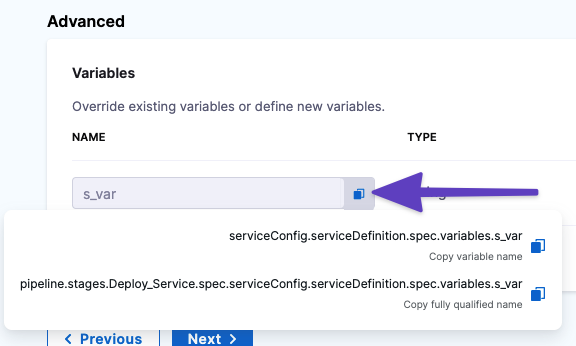
There are two options:
- Copy variable name: use this option if you will only be referencing this variable in the current stage. Expression:
<+serviceConfig.serviceDefinition.spec.variables.[name]>
- Copy fully qualified name: use this option if you will be referencing this variable in another stage. Example:
<+pipeline.stages.[stage_name].spec.serviceConfig.serviceDefinition.spec.variables.[name]>
You can use these expressions in any setting in your pipeline. Select the expression option and enter the expression.
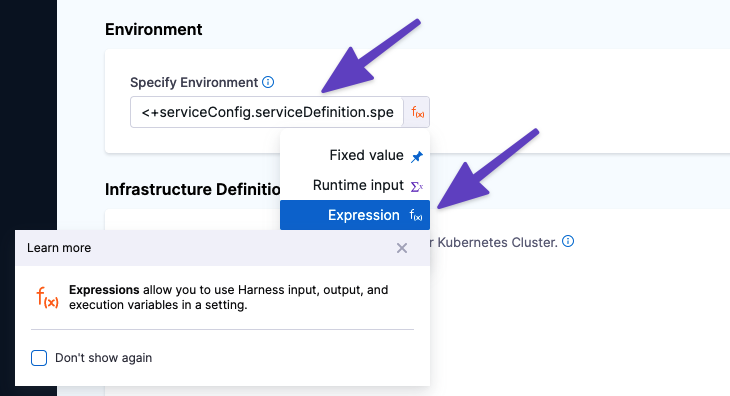
To override the service variable in a script, reference its name and use a new value.
<+service.name>
The name of the service where the expression is evaluated.
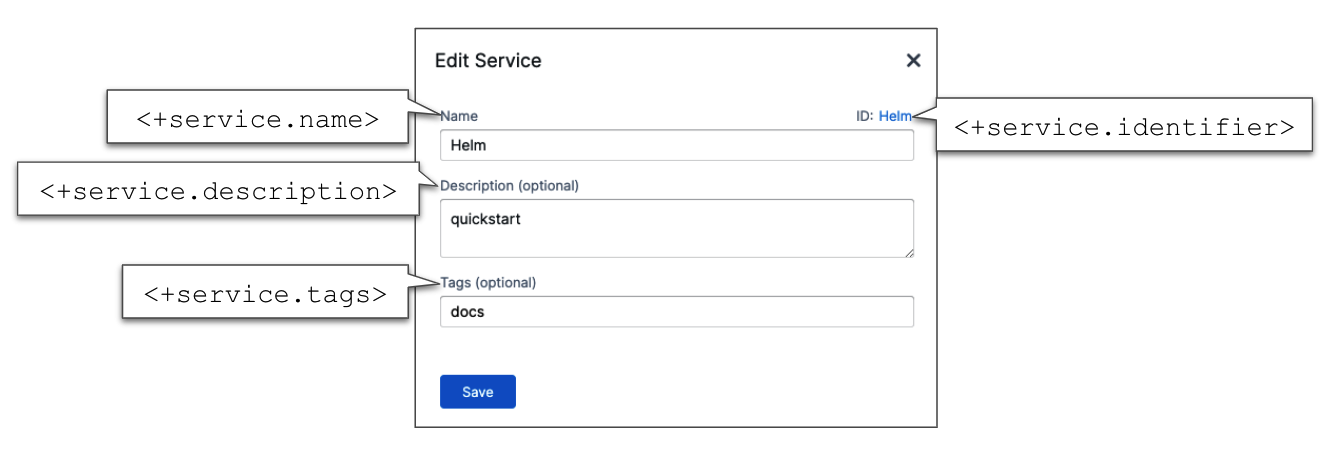
<+service.description>
The description of the service where the expression is evaluated.
<+service.tags>
The tags on the service where the expression is evaluated.
To reference a specific tag use <+service.tags.[tag_key]>.
<+service.identifier>
The entity identifier of the service where the expression is evaluated.
<+service.type>
Resolves to stage service type, such as Kubernetes.
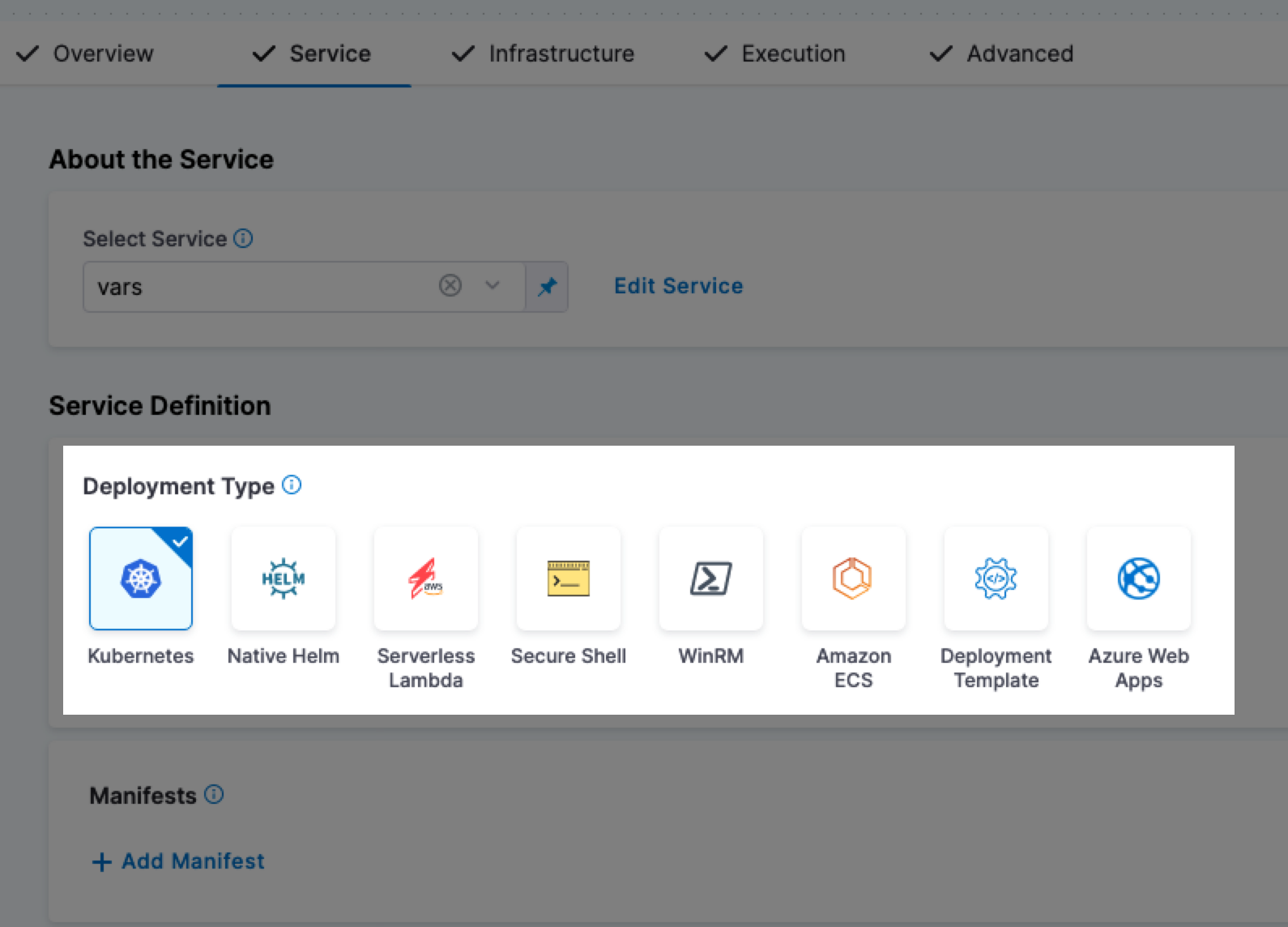
<+service.gitOpsEnabled>
Resolves to a boolean value to indicate whether the GitOps option is enabled (true) or not (false).
For details on using the GitOps option, go to Harness GitOps ApplicationSet and PR Pipeline Tutorial.
Manifest
There are generic and deployment type-specific expressions for manifests.
Manifest settings are referenced by name.
You can always determine the expressions you can use by looking at the service YAML.
For example, the expression <+manifests.mymanifest.valuesPaths> can be created by using the manifest name and the valuesPaths key in the YAML.
...
manifests:
- manifest:
identifier: mymanifest
type: K8sManifest
spec:
store:
type: Harness
spec:
files:
- account:/Templates
valuesPaths:
- account:/values.yaml
skipResourceVersioning: false
...
Let's look at a few generic manifest expressions.
<+manifests.[manifest name].identifier>
Resolves to the manifest Id in Harness.
...
manifests:
- manifest:
identifier: mymanifest
...
<+manifests.[manifest name].type>
Resolves to the manifest type. For example, K8sManifest.
...
manifests:
- manifest:
identifier: mymanifest
type: K8sManifest
...
<+manifests.[manifest name].store>
Resolves to where the manifest is stored. For example, this manifest is stored in the Harness File Store.
...
manifests:
- manifest:
identifier: mymanifest
type: K8sManifest
spec:
store:
type: Harness
spec:
files:
- account:/Templates
...
<+manifest.identifier.commitID>
The commit ID of the manifests used in a service. This is captured in the output section of a deployment step.
You can copy the expressions for the name and value of commitID.
For example:
Name: <+pipeline.stages.satr.spec.execution.steps.rolloutDeployment.output.manifest.values.commitId>
Value: 8d30fc49e6ed13155590b7d8c16931cd1a7b5bac
Artifact
If an artifact expression is in a manifest or step and you have not selected an artifact in a service definition, or set the artifact is set as a runtime Input, you will be prompted to select an artifact at runtime. This is true even if the stage does not deploy an artifact (such as a custom stage or a stage performing a Kustomize deployment).
For example, here is how the common artifact expressions resolve for a Kubernetes deployment with a Docker image on Docker Hub:
- <+artifacts.primary.tag>:
stable - <+artifacts.primary.image>:
index.docker.io/library/nginx:stable - <+artifacts.primary.imagePath>:
library/nginx - <+artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret>:
secret-value - <+artifacts.primary.dockerConfigJsonSecret>:
secret-value - <+artifacts.primary.type>:
DockerRegistry - <+artifacts.primary.connectorRef>:
DockerHub
Example output for all artifact expressions
Here's an example where we use a Shell Script step to echo all the artifact expressions.
echo "artifacts.primary.image: "<+artifacts.primary.image>
echo "artifacts.primary.connectorRef: "<+artifacts.primary.connectorRef>
echo "artifacts.primary.digest: "<+artifacts.primary.digest>
echo "artifacts.primary.identifier: "<+artifacts.primary.identifier>
echo "artifacts.primary.imagePath: "<+artifacts.primary.imagePath>
echo "artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret: "<+artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret>
echo "artifacts.primary.label: "<+artifacts.primary.label>
echo "artifacts.primary.metadata: "<+artifacts.primary.metadata>
echo "artifacts.primary.primaryArtifact: "<+artifacts.primary.primaryArtifact>
echo "artifacts.primary.tag: "<+artifacts.primary.tag>
echo "artifacts.primary.type: "<+artifacts.primary.type>
Here's the output:
Executing command ...
artifacts.primary.image: index.docker.io/johndoe/tweetapp:21
artifacts.primary.connectorRef: Docker_Hub_with_Pwd
artifacts.primary.digest: null
artifacts.primary.identifier: primary
artifacts.primary.imagePath: johndoe/tweetapp
artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret: 123abc
artifacts.primary.metadata: {image=index.docker.io/johndoe/tweetapp:21, tag=21}
artifacts.primary.primaryArtifact: true
artifacts.primary.tag: 21
artifacts.primary.type: DockerRegistry
Command completed with ExitCode (0)
<+artifacts.primary.tag>
Not Harness tags. This expression evaluates to the tags on the artifact pushed, pulled, or deployed. For example, AMI tags. If you are deploying the Docker image nginx:stable-perl, the tag would be stable-perl.
<+artifacts.primary.image>
The full location to the Docker image. For example, docker.io/bitnami/nginx:1.22.0-debian-11-r0.
For non-containerized artifacts, use <+artifacts.primary.path>, described below. To see just the image name, use <+artifacts.primary.imagePath>.
Use <+artifacts.primary.image> or <+artifacts.primary.imagePath> in your values YAML file when you want to deploy an artifact you have added to the Artifacts section of a CD stage service definition.
For example, here is the Artifacts section with an artifact:
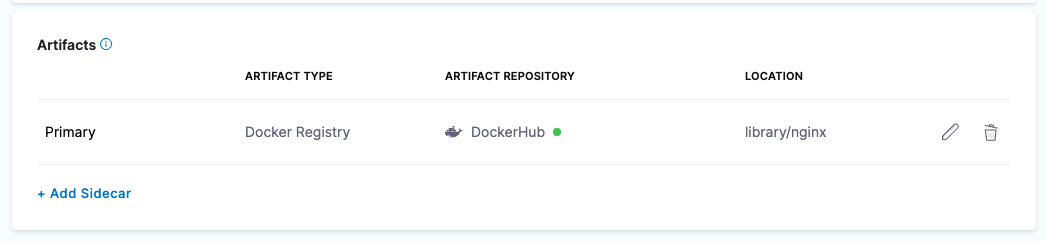
Here is the Values YAML file referencing the artifact in Artifacts:
name: example
replicas: 2
image: <+artifacts.primary.image>
# dockercfg: <+artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret>
createNamespace: true
namespace: <+infra.namespace>
...
For more information, go to Example Kubernetes Manifests using Go Templating.
<+artifacts.primary.path>
The full path to the non-containerized artifact. This expression is used in non-containerized deployments.
<+artifacts.primary.filePath>
The file name of the non-containerized artifact. This expression is used in non-containerized deployments. For example, a ZIP file in AWS S3.
<+artifacts.primary.imagePath>
The image name, such as nginx. To see the entire image location use <+artifacts.primary.image>.
<+artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret>
If some cases, your Kubernetes cluster might not have the permissions needed to access a private Docker registry. For these cases, the values.yaml or manifest file in service definition Manifests section must use the dockercfg parameter.
If the Docker image is added in the service definition Artifacts section, you can reference it as dockercfg: <+artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret>.
values.yaml:
name: <+stage.variables.name>
replicas: 2
image: <+artifacts.primary.image>
dockercfg: <+artifacts.primary.imagePullSecret>
createNamespace: true
namespace: <+infra.namespace>
...
Go to Pull an Image from a Private Registry for Kubernetes for more information.
<+artifacts.primary.dockerConfigJsonSecret>
In some cases, your Kubernetes cluster might not have the permissions needed to access a private Docker registry. For such cases, the values.yaml or manifest files in the service definition Manifests section must use the dockerconfigjson parameter.
If the Docker image is added in the service definition Artifacts section, you can reference it as dockerconfigjson: <+artifact.dockerConfigJsonSecret>.
Here is a sample values.yaml:
name: <+stage.variables.name>
replicas: 2
image: <+artifacts.primary.image>
dockerconfigjson: <+artifacts.primary.dockerConfigJsonSecret>
createNamespace: true
namespace: <+infra.namespace>
...
For more information, go to Pull an Image from a Private Registry for Kubernetes.
<+artifacts.primary.type>
The type of repository used to add this artifact in the service Artifacts. For example, Docker Hub, ECR, or GCR.
<+artifacts.primary.connectorRef>
The entity identifier for the connector used to connect to the artifact repository.
<+artifacts.primary.label.get("")>
This expression resolves to the Docker labels of a Docker image.
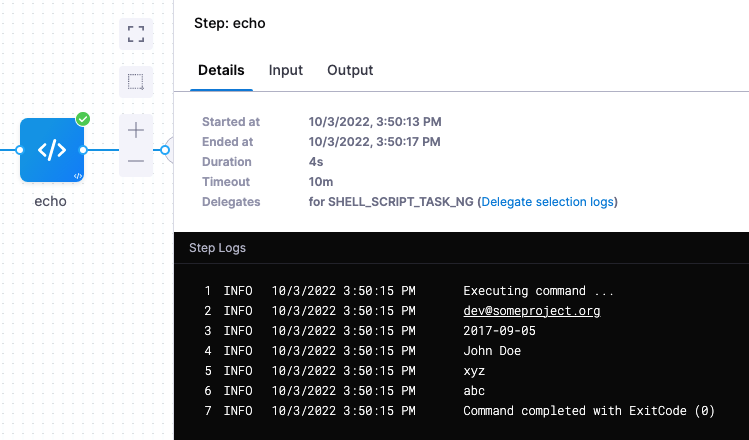
For example, here are the labels for a Docker image:
maintainer=dev@someproject.orgbuild_date=2017-09-05multi.author=John Doekey-value=xyzmulti.key.value=abc
In a Harness Shell script step or any setting where you want use the labels, you can reference them.
echo <+artifacts.primary.label.get("maintainer")>
echo <+artifacts.primary.label.get("build_date")>
echo <+artifacts.primary.label.get("multi.author")>
echo <+artifacts.primary.label.get("key-value")>
echo <+artifacts.primary.label.get("multi.key.value")>
When you run the pipeline, the expressions will resolve to their respective label values.
<+artifact.primary.identifier>
The Id of the Primary artifact added in a Service Artifacts section.

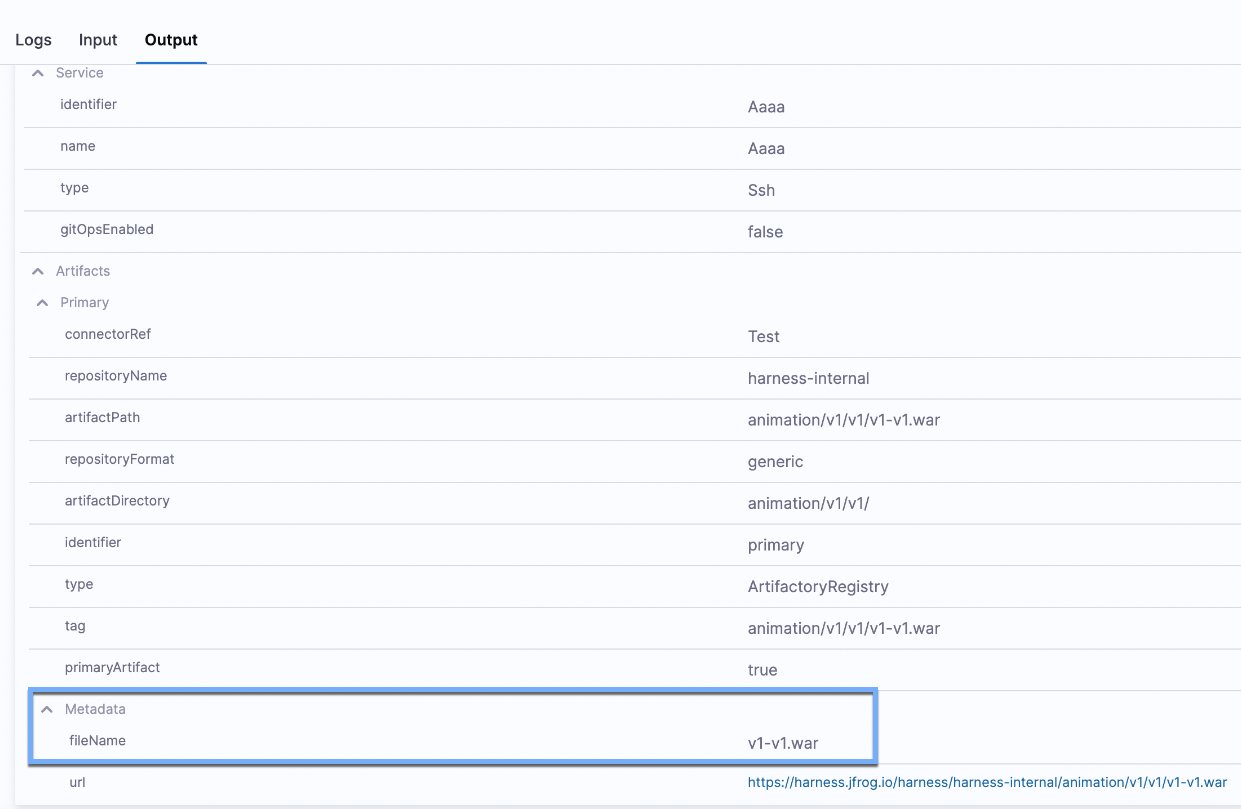
<+artifact.metadata.fileName>
The file name of the Artifactory artifact.
This variable is added to the metadata of the Artifactory artifacts with generic repository format. You can view this variable in the Output tab of the Service step of a pipeline execution.
Sidecar artifacts
Sidecar artifact expressions use the Sidecar Identifier to reference the sidecar artifact.
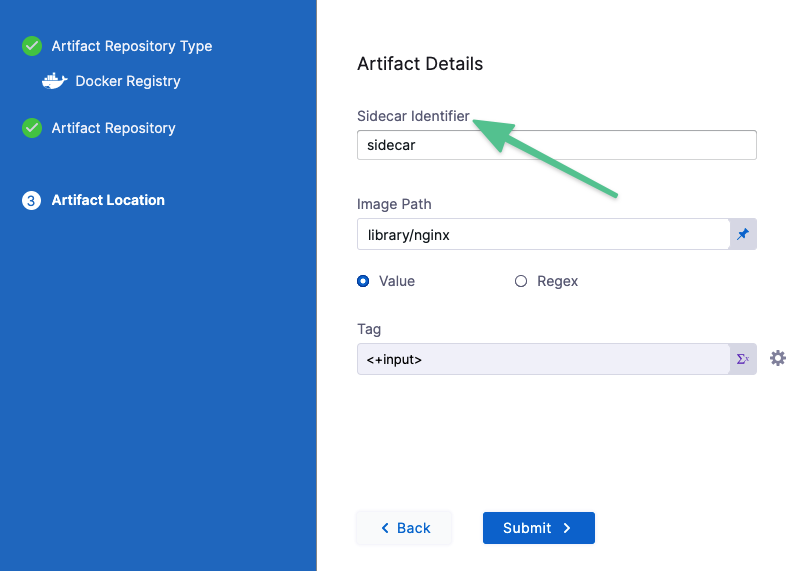
The sidecar identifier is set when you add the sidecar artifact. You can see it in the artifact listing.
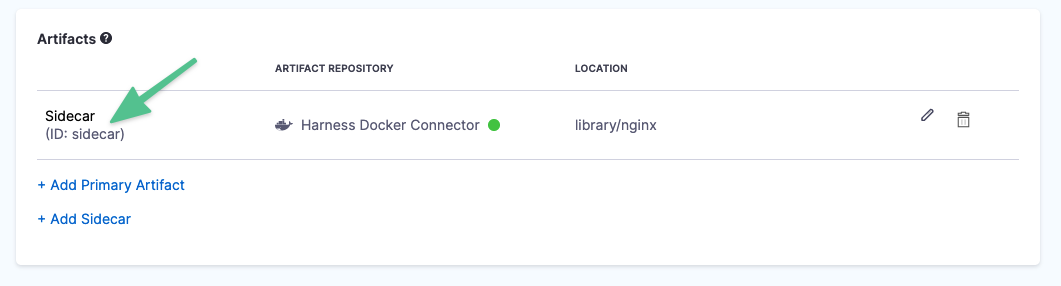
Here are the sidecar expressions:
<+artifacts.sidecars.[sidecar_identifier].imagePath><+artifacts.sidecars.[sidecar_identifier].image><+artifacts.sidecars.[sidecar_identifier].type><+artifacts.sidecars.[sidecar_identifier].tag><+artifacts.sidecars.[sidecar_identifier].connectorRef>
Environment
Environment-level variables for service v2
Currently, there are two versions of services and environments, v1 and v2. Services and environments v1 are being replaced by services and environments v2.
The use of variable expressions is different between v1 and v2.
For more information, go to Services and Environments Overview.
To reference an environment-level variable, use the expression <+env.variables.[variable name]>.
For example, here is an environment variable named envvar.
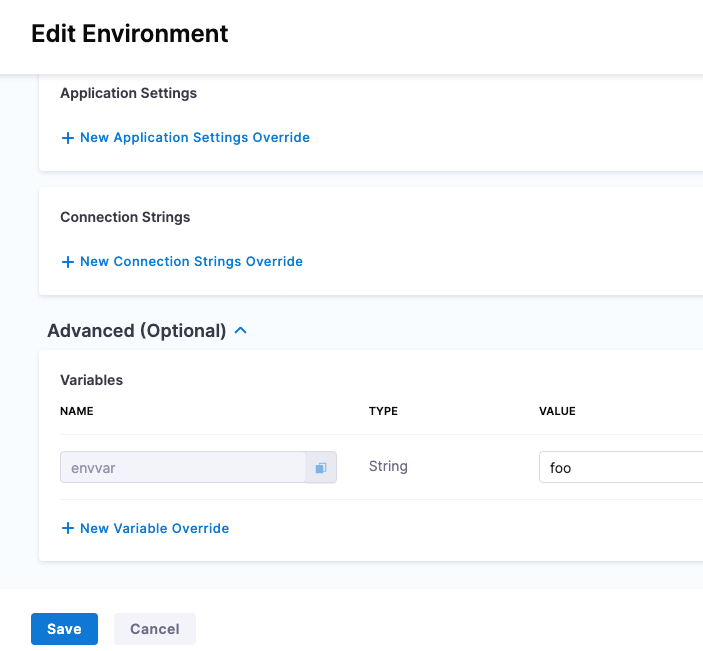
You would reference it as <+env.variables.envvar>.
<+env.name>
The name of the stage environment.
<+env.identifier>
The entity identifier of the stage's environment.
<+env.description>
The description of the environment.
<+env.type>
The environment type, such as Production or PreProduction.
The available values are:
PreProductionProduction
<+env.envGroupName>
The name of the environment group to which the environment belongs (if defined).
<+env.envGroupRef>
The environment group reference.
You can evaluate the expression using JEXL in the Conditional Execution settings of steps or stages:
<+env.type> != "Production"
Environment expressions can be used in service steps as well.
Infrastructure
The following expressions provide information about the pipeline infrastructure settings. The infrastructure in a pipeline is the Infrastructure Definition in the Harness environment used in the CD stage's Environment section.
<+infra.name>
The name of the infrastructure definition used in the pipeline stage.
<+infra.connectorRef>
The Id of the connector used in the infrastructure definition.
<+infra.connector.name>
The name of the connector used in the infrastructure definition.
<+INFRA_KEY>
The infrastructure key. The key is a unique string that identifies a deployment target infrastructure. It is typically used in the Release Name setting to add labels to release for tracking.
For example, in the infrastructure definition of a deploy stage, the <+INFRA_KEY> is used in the Release Name to give the release a unique name.
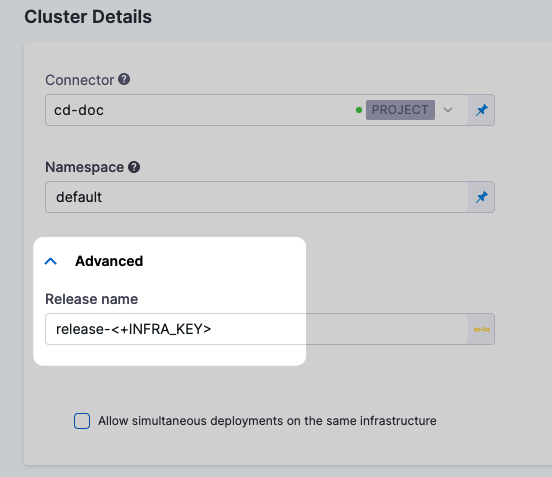
When you deploy, Harness adds the release name as a label. For example, in a Kubernetes deployment you can see harness.io/release-name=release-2f9eadcc06e2c2225265ab3cbb1160bc5eacfd4f.
...
Pod Template:
Labels: app=hello
deployment=hello
harness.io/release-name=release-2f9eadcc06e2c2225265ab3cbb1160bc5eacfd4f
Containers:
the-container:
Image: monopole/hello:1
...
Harness can now track the release for comparisons and rollback.
<+infra.namespace>
The namespace used in the infrastructure definition.
<+infra.releaseName>
The release name used in the infrastructure definition.
Step
The following instance expressions are for stage steps.
<+step.name>
The step name.
<+step.identifier>
The step identifier.
<+step.executionUrl>
The execution URL of the step. This is the same URL you see in your browser when you are viewing the pipeline execution.
Use the following fully qualified expression to get the execution URL for a specific step in the pipeline:
<+pipeline.stages.[stageId].spec.execution.steps.[stepid].executionUrl>
Instances
The following instance expressions are supported in SSH, WinRM, and custom deployments using deployment templates. These deployments can be done on physical data centers, AWS, and Azure.
For details on these deployment types, go to Secure Shell (SSH) deployment tutorial, WinRM deployment tutorial, and Custom deployments using Deployment Templates tutorial.
To use these instance expressions in a step, you must use the repeat Looping Strategy and identify all the hosts for the stage as the target.
repeat:
items: <+stage.output.hosts>
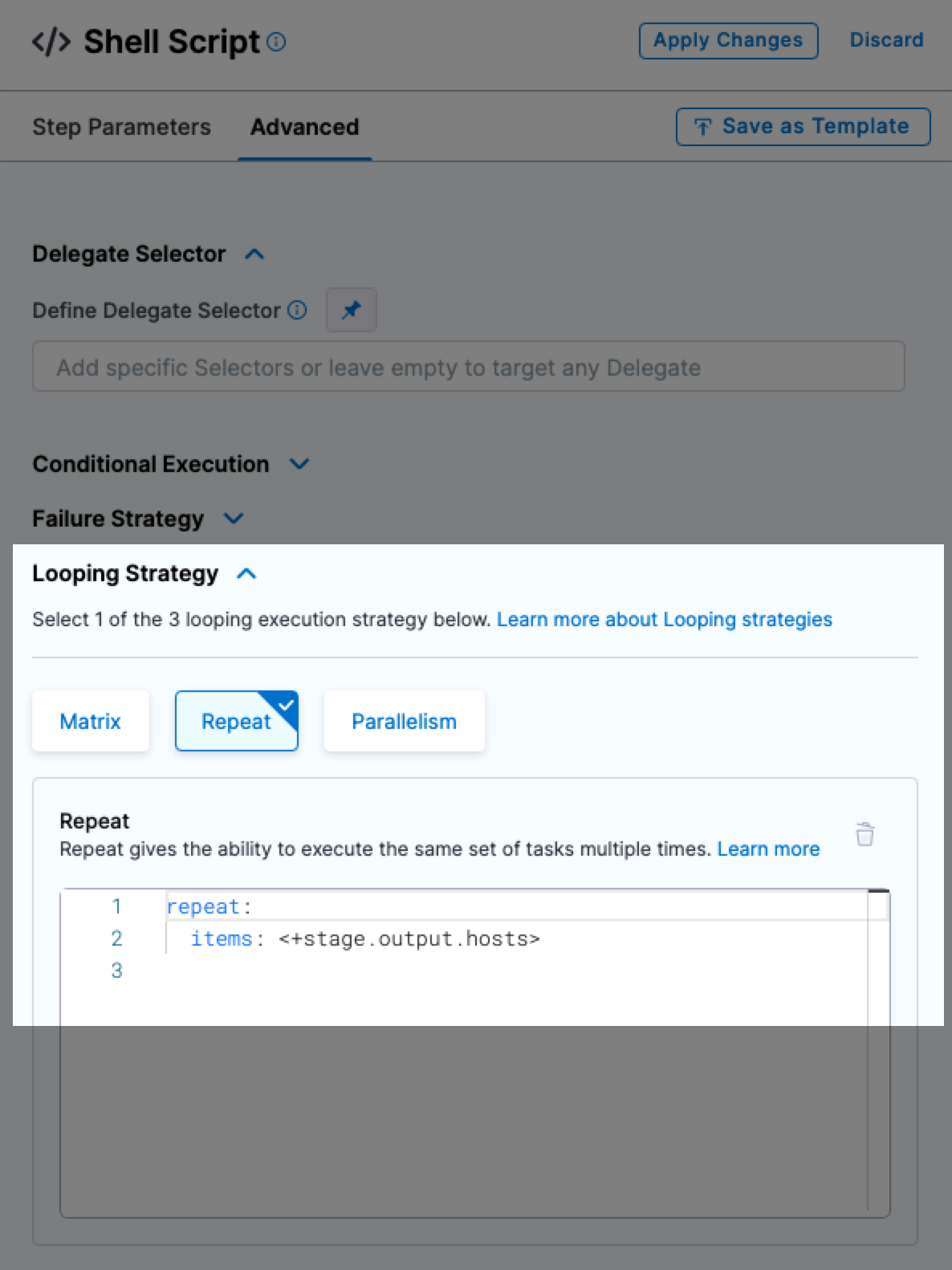
For examples, see Run a script on multiple target instances.
For Microsoft Azure, AWS, or any platform-agnostic Physical Data Center (PDC):
<+instance.hostName><+instance.host.instanceName><+instance.name>
For Microsoft Azure or AWS:
<+instance.host.privateIp><+instance.host.publicIp>
Deployment templates
For Deployment Templates, you can use <+instance...> expressions to reference host(s) properties.
The <+instance...> expressions refer to the Instance Attributes in the deployment template:
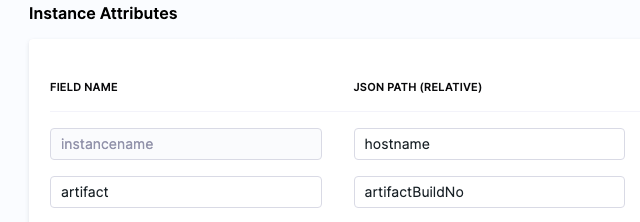
The following expressions refer to instance(s) collected by the mandatory instancename field.
<+instance.hostName><+instance.host.instanceName><+instance.name>
The expression <+instance.host.properties.[property name]> can used to reference the other properties you added to Instance Attributes.
For example, in the example above you can see the artifact field name mapped to the artifactBuildNo property.
To reference artifact you would use <+instance.host.properties.artifact>.
instance.name has the same value as instance.hostName. Both are available for backward compatibility.
<+instance.hostName>
The host/container/pod name where the microservice/application is deployed.
If you use this variable in a pipeline, such as in a Shell script step, Harness will apply the script to all target instances. You do not have to loop through instances in your script.
<+instance.host.instanceName>
The same as <+instance.hostName>.
<+instance.name>
The name of the instance on which the service is deployed.
If you use this variable in a pipeline, such as in a Shell script step, Harness will apply the script to all target instances. You do not have to loop through instances in your script.
<+instance.host.privateIp>
The private IP of the host where the service is deployed.
If you use this variable in a pipeline, such as in a Shell script step, Harness will apply the script to all target instances. You do not have to loop through instances in your script.
<+instance.host.publicIp>
The public IP of the host where the service is deployed.
If you use this variable in a pipeline, such as in a Shell script step, Harness will apply the script to all target instances. You do not have to loop through instances in your script.
Triggers
<+trigger.artifact.build>
Resolves to the artifact version (such as a Docker Tag) that initiated an On New Artifact Trigger.
When you add a new artifact trigger, you select the artifact to listen on, and its Tag setting is automatically populated with <+trigger.artifact.build>.
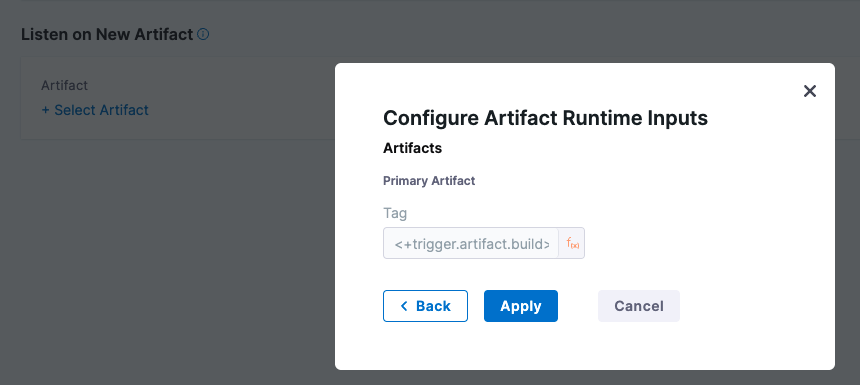
The <+trigger.artifact.build> used for Tag makes sure that the new artifact version that executed the trigger is used for the deployment.
Adding a new tag to the artifact fires the trigger and executes the pipeline. Harness resolves <+trigger.artifact.build> to the tag that fired the trigger. This makes sure that the new tag is used when pulling the artifact and the new artifact version is deployed.
Git trigger and payload expressions
Harness includes built-in expressions for referencing trigger details such as a PR number.
For example:
<+trigger.type>- Webhook.
<+trigger.sourceRepo>- Github, Gitlab, Bitbucket, Custom
<+trigger.event>- PR, PUSH, etc.
For a complete list, see Triggers Reference.
Triggers and RBAC
Harness RBAC is applied to triggers in Harness, but it is not applied to the repositories used by the triggers.
For example, you might have an On New Artifact Trigger that is started when a new artifact is added to the artifact repo. Or a Webhook Trigger that is started when a PR is merged.
You can select who can create and use these triggers within Harness. However, you must use your repository's RBAC to control who can add the artifacts or initiate events that start the Harness trigger.
Kubernetes
${HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH}
The path to a Harness-generated kubeconfig file containing the credentials you provided to Harness. The credentials can be used by kubectl commands by exporting its value to the KUBECONFIG environment variable.
Harness only generates this kubeconfig file when a delegate is outside of the target cluster and is making a remote connection. When you set up the Kubernetes cluster connector to connect to the cluster, you select the Specify master URL and credentials option. The master URL and credentials you supply in the connector are put in the kubeconfig file and used by the remote delegate to connect to the target cluster.
Consequently, you can only use ${HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH} when you are using a delegate outside the target cluster and a Kubernetes cluster connector with the Specify master URL and credentials option.
If you are running the script using an in-cluster delegate with the Use the credentials of a specific Harness Delegate credentials option, then there are no credentials to store in a kubeconfig file since the Delegate is already an in-cluster process.
You can use this variable in a Shell script step to set the environment variable at the beginning of your kubectl script:
export KUBECONFIG=${HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH}
For example:
export KUBECONFIG=${HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH} kubectl get pods -n default
The ${HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH} expression can be used in scripts in Shell script steps. It cannot be used in other scripts such as a Terraform script.
kubernetes.release.revision
Harness expression for the deployment revision number.
You can use the expression <+kubernetes.release.revision> in values.yaml, OpenShift Params, and Kustomize Patches.
This will help you to:
- Reference the current Harness release number as part of your manifest.
- Reference versioned ConfigMaps and Secrets in custom resources and fields unknown by Harness.
Important: Users must update their delegate to version 1.0.79100 to use this expression.
Tag expressions
You can reference tags using Harness expressions.
You simply reference the tagged entity and then use tags.[tag name], like <+pipeline.tags.docs>
For example, here are several different references:
<+pipeline.tags.[tag name]><+stage.tags.[tag name]><+pipeline.stages.s1.tags.[tag name]><+serviceConfig.service.tags.[tag name]>
Migrating FirstGen expressions to NextGen
When migrating Harness FirstGen expressions to Harness NextGen, review the following table.
All FirstGen expressions use the ${...} format. For example, ${approvedBy.name}. In NextGen, this has been replaced by <+...>. For example, <+approvedBy.name>.
| FirstGen | Next Gen |
|---|---|
| Approvals | Approvals |
| approvedBy.name | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.HarnessApproval.output.approvalActivities[0].user.name |
| approvedBy.email | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.HarnessApproval.output.approvalActivities[0].user.email |
| HTTP Step | HTTP Step |
| httpResponseCode | httpResponseCode |
| httpResponseBody | httpResponseBody |
| httpMethod | httpMethod |
| httpUrl | httpUrl |
| httpResponseMethod | pipeline.stages.HTTP.spec.execution.steps.[step_Id].output.httpMethod |
| httpResponseCode | pipeline.stages.HTTP.spec.execution.steps.[step_Id].output.httpResponseCode |
| httpResponseBody | pipeline.stages.HTTP.spec.execution.steps.[step_Id].output.httpResponseBody |
| Artifacts | Artifacts |
| artifact.metadata.image | artifact.image |
| artifact.source.dockerconfig | artifact.imagePullSecret |
| artifact.serviceIds | NA |
| artifact.metadata.tag | artifact.tag |
| artifact.url | artifact.metadata.url |
| artifact.buildNo | artifact.tag |
| artifact.metadata.image | artifact.imageartifact.image. Path for sidecar artifact: artifacts.sidecars.sidecarId.[property] |
| artifact.metadata.[KEY] | artifact.metadata.[KEY] |
| artifact.displayName | |
| artifact.description | NA |
| artifact.source.username | NA |
| artifact.source.registryUrl | Dependent on artifact source type: artifact.docker.repositoryUrlartifact.gcr.repositoryUrl |
| artifact.source.repositoryName | Dependent on artifact source type: artifact.docker.repositoryName |
| artifact.label.label-key | |
| artifact.revision | artifact.tag |
| artifact.metadata.artifactId | artifact.metadata.artifactId |
| artifact.bucketName | artifact.metadata.bucketName |
| artifact.key | artifact.metadata.key |
| artifact.buildFullDisplayName | |
| artifact.artifactPath | artifact.metadata.artifactPath |
| artifact.metadata.repositoryName | artifact.metadata.repositoryName |
| artifact.metadata.harness | artifact.metadata.harness |
| artifact.metadata.groupId | artifact.metadata.groupId |
| artifact.fileName | artifact.metadata.fileName |
| artifact.label.get("[label-key]") | |
| artifact.metadata.getSHA() | artifact.metadata.SHA |
| Application | Application (account, org, project) |
| app.name | account.nameaccount.companyNameorg.nameproject.nameproject.identifier |
| app.description | project.descriptionorg.description |
| app.accountId | account.identifier |
| app.defaults.[variable_name] | variable.[variable_Id] |
| Service | Service |
| service.name | service.name |
| service.description | service.description |
| serviceVariable.[var_name] | serviceVariables.[var_name] |
| service.manifest | manifest.name |
| service.manifest.repoRoot | manifest.repoName |
| Environment | Environment |
| env.description | FQN: stages.[stage_Id].spec.infrastructure.environment.name. Alias: env.description. FQN: stages.[stage_Id].spec.infrastructure.environment.description |
| env.environmentType | env.type |
| env.name | env.name |
| env.accountId | account.identifier |
| env.keywordsenvironmentVariable.variable_name | env.variables.var_name |
| Infrastructure | Infrastructure |
| infra.kubernetes.namespace | infra.namespace or infra.releaseName. FQN: stages.[stage_Id].spec.infrastructure.infrastructureDefinition.spec.namespace |
| infra.route | |
| infra.tempRoute | |
| infra.name | infra.name |
| infra.cloudProvider.name | infra.connectorRef |
| Workflow | Workflow (Stage level expressions) |
| workflow.releaseNo | stage.identifier |
| workflow.lastGoodReleaseNo | N/A |
| workflow.lastGoodDeploymentDisplayName | N/A |
| workflow.displayName | stage.namepipeline.name |
| workflow.description | stage.descriptionpipeline.description |
| workflow.pipelineResumeUuid | NA |
| workflow.pipelineDeploymentUuid | pipeline.executionIdpipeline.sequenceId |
| workflow.startTs | pipeline.startTs |
| workflow.variables.[var_name] | pipeline.variables.[var_name] or stage.variables.[var_name] |
| timestampId | |
| deploymentUrl | pipeline.execution.url |
| context.published_name.var_name | |
| deploymentTriggeredBy | pipeline.triggeredBy.namepipeline.triggeredBy.email |
| currentStep.name | step.name |
| regex.extract("v[0-9]+.[0-9]+", artifact.fileName) | N/A |
| currentStep.type | N/A |
| Pipeline Variables | Pipeline Variables |
| pipeline.name | pipeline.name |
| deploymentUrl | pipeline.execution.url |
| deploymentTriggeredBy | pipeline.triggeredBy.namepipeline.triggeredBy.email |
| Rollback Artifact Variables | Rollback Artifact Variables |
| rollbackArtifact.url | NA |
| rollbackArtifact.buildNo | artifact.tagrollback, artifact.imagerollback, artifact.imagePathrollback, artifact.typerollback, artifact.connectorRef, for sidecar artifact: rollbackArtifact.sidecars.sidecar_Id.[property] |
| rollbackArtifact.buildFullDisplayName | |
| rollbackArtifact.ArtifactPath | |
| rollbackArtifact.description | |
| rollbackArtifact.displayName | |
| rollbackArtifact.fileName | |
| rollbackArtifact.key | |
| rollbackArtifact.metadata.image | rollbackArtifact.image |
| rollbackArtifact.metadata.tag | rollbackArtifact.tag |
| rollbackArtifact.source.registryUrl | |
| Instance | Instance |
| instance.name | instance.name |
| instance.hostName | instance.hostName |
| instance.host.hostName | instance.host.hostName |
| instance.host.ip | instance.host.privateIpinstance.host.publicIp. The privateIp and publicIp are supported for Azure, AWS, SSH/WinRM deployments. |
| instance.dockerId | TBD |
| instance.host.publicDns | NA |
| instance.EcsContainerDetails.completeDockerId | pipeline.stages.[stage_identifier].spec.execution.steps.[step_identifier].steps.[step_identifier].deploymentInfoOutcome.serverInstanceInfoList[x].containers[x].runtimeId |
| instance.ecsContainerDetails.taskId | pipeline.stages.[stage_identifier].spec.execution.steps.[step_identifier].steps.[step_identifier].deploymentInfoOutcome.serverInstanceInfoList[x].taskArn |
| instance.ecsContainerDetails.taskArn | pipeline.stages.[stage_identifier].spec.execution.steps.[step_identifier].steps.[step_identifier].deploymentInfoOutcome.serverInstanceInfoList[x].taskArn |
| [step__name].serviceName | N/A |
| ECSServiceSetup.serviceName | service.nameThis expression only works if customer chooses to use this in service definition manifest as wellorpipeline.stages.ecs.spec.execution.steps.[Step ID].output.serviceName |
| ECSServiceSetup.clusterName | infra.cluster |
| instance.EcsContainerDetails.dockerId | pipeline.stages.[stage_identifier].spec.execution.steps.[step_identifier].steps.[step_identifier].deploymentInfoOutcome.serverInstanceInfoList[x].containers[x].runtimeId |
| Host (Deprecated) All host properties are available using Instance | Host (Deprecated) All host properties are available using Instance |
| host.name | |
| host.ip | |
| host.publicDns | |
| host.ec2Instance.instanceId | |
| host.ec2Instance.instanceType | |
| host.ec2Instance.imageId | |
| host.ec2Instance.architecture | |
| host.ec2Instance.kernelId | |
| host.ec2Instance.keyName | |
| host.ec2Instance.privateDnsName | |
| host.ec2Instance.privateIpAddress | |
| host.ec2Instance.publicDnsName | |
| host.ec2Instance.publicIpAddress | |
| host.ec2Instance.subnetId | |
| host.ec2Instance.vpcId | |
| host.hostName | |
| Terraform | Terraform |
| terraform.clusterName | [step_Id].output.[output_name]. For example: pipeline.stages.stage1.spec.execution.steps.TerraformApply.output.clusterName |
| terraformApply.tfplan | |
| terraformDestroy.tfplan | |
| terraformPlan.jsonFilePath() | execution.steps.[Terraform Plan step Id].plan.jsonFilePath. For example: execution.steps.terraformPlan.plan.jsonFilePath |
| terraformPlan.destroy.jsonFilePath() | execution.steps.[Terraform Plan step Id].plan.jsonFilePath For example: execution.steps.terraformPlan.plan.jsonFilePath |
| terraformApply.add | |
| terraformApply.change | |
| terraformApply.destroy | |
| terraformDestroy.add | |
| terraformDestroy.change | |
| terraformDestroy.destroy | |
| terraformApply.tfplanHumanReadable | execution.steps.[Terraform Plan step Id].plan.humanReadableFilePath. For example: execution.steps.terraformPlan.plan.humanReadableFilePath |
| terraformDestroy.tfplanHumanReadable | execution.steps.[Terraform Plan step Id].plan.humanReadableFilePath. For example: execution.steps.terraformPlan.plan.humanReadableFilePath |
| terraform.[output_name] | pipeline.stages.[stage-Id].spec.execution.steps.TerraformApply.output.[output_name] |
| CloudFormation | CloudFormation |
| cloudformation.[output_name] | pipeline.stages.stage1.spec.execution.steps.CreateStack.output.[output_name] |
| cloudformation.region | pipeline.stages.stage1.spec.execution.steps.CreateStack.output.region |
| HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH | HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH |
| infra.kubernetes.infraId | N/A |
| Helm | Helm |
| infra.helm.releaseNameservice.name-env.name-infra.helm.shortId | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.infrastructure.infrastructureDefinition.spec.output.releaseName, pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.rolloutDeployment.deploymentInfoOutcome.serverInstanceInfoList[2].releaseName |
| infra.helm.shortId | N/A |
| helmChart.description | service.description |
| helmChart.displayName | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.serviceConfig.output.manifestResults.[service_Id].chartName |
| helmChart.metadata.basePath | N/A |
| helmChart.metadata.bucketName | N/A |
| helmChart.metadata.repositoryName | N/A |
| helmChart.metadata.url | N/A |
| helmChart.name | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.rolloutDeployment.output.releaseName |
| helmChart.version | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.serviceConfig.output.manifestResults.[service_Id].helmVersion |
| Nested Expression: secrets.getValue("terraform-aws-env_name-id") | secrets.getValue("test_secret" + pipeline.variables.envVar), or secrets.getValue("test_secret".concat(pipeline.variables.envVar)) |
| Email Step | Email Step |
| toAddress | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.[step_Id].spec.to |
| ccAddress | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.[step_Id].spec.cc |
| subject | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.[step_Id].spec.subject |
| body | pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.[step_Id].spec.body |
| AMI | AMI |
| ami.newAsgName | Rolling: pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.AsgRollingDeployStep.output.asg.autoScalingGroupName. Blue Green: pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.AsgRollingDeployStep.output.prodAsg.autoScalingGroupName |
| ami.oldAsgName | Rolling: pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.AsgRollingDeployStep.output.asg.autoScalingGroupName. Blue Green: pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.AsgRollingDeployStep.output.stageAsg.autoScalingGroupName |
| Tanzu Application Services | Tanzu Application Services |
| pcf.finalRoutes | pcf.finalRoutes |
| pcf.oldAppRoutes | pcf.oldAppRoutes |
| pcf.tempRoutes | pcf.tempRoutes |
| pcf.newAppRoutes | pcf.newAppRoutes |
| pcf.newAppRoutes[0] | pcf.newAppRoutes[0] |
| pcf.newAppName | pcf.newAppName |
| pcf.newAppGuid | pcf.newAppGuid |
| pcf.oldAppName | pcf.oldAppName |
| pcf.activeAppName | pcf.activeAppName |
| pcf.inActiveAppName | pcf.inActiveAppName |
| pcf.oldAppGuid | pcf.oldAppGuid |
| pcf.oldAppRoutes[0] | pcf.oldAppRoutes[0] |
| infra.pcf.cloudProvider.name | infra.connector.name |
| infra.pcf.organization | infra.organization |
| infra.pcf.space | infra.space |
| host.pcfElement.applicationId | pcf.newAppGuid |
| host.pcfElement.displayName | Basic or Canary deployment: pcf.newAppName. Blue Green deployment: pcf.inActiveAppName |
| host.pcfElement.instanceIndex | |
| CONFIG File | CONFIG File |
| configFile.getAsString("cf_file") | |
| configFile.getAsBase64("cf_file") | |
| configFile.getAsString("cf_secret") | |
| configFile.getAsBase64("cf_secret") | |
| fileStore.getAsString("/folder1/configFileProject") | |
| fileStore.getAsBase64("account:/folder1/folder2/ConfigFile") |
For more information migrating to NextGen, go to the following: