Add account, org, and project-level variables
In your Pipelines, Variables can be added at the Pipeline-level, which makes them available to all Stages in the Pipeline. Within a Stage, you can add Variables at the Stage and Service-level. Here's a video covering those Variable types.
But what about when you need to use the same Variable across multiple Pipelines, or even Pipelines in multiple Projects?
With Account-level, Org-level, and Project-level Variables, Harness lets you store values that you can share and use across multiple Pipelines in multiple Projects.
This topic explains how to add Variables as an Account-level and Org-level Resource in Harness.
For details on Harness built-in variables, see Built-in Harness Variables Reference.
Before you begin
Make sure you have all permissions on Variables to add and manage Variables.

Limitations
- Harness supports only String type Account-level, Org-level, and Project-level Variables. This is only a temporary limitation. You can use Secrets in Pipeline, Stage, and Service variables.
- If you delete a Variable that is referenced using expressions in entities like Pipelines, the reference expressions are not deleted. At runtime, when the expressions are resolved, the expression will resolve as null.
Visual Summary
Here is a quick overview of how Variables can be shared across Pipelines.
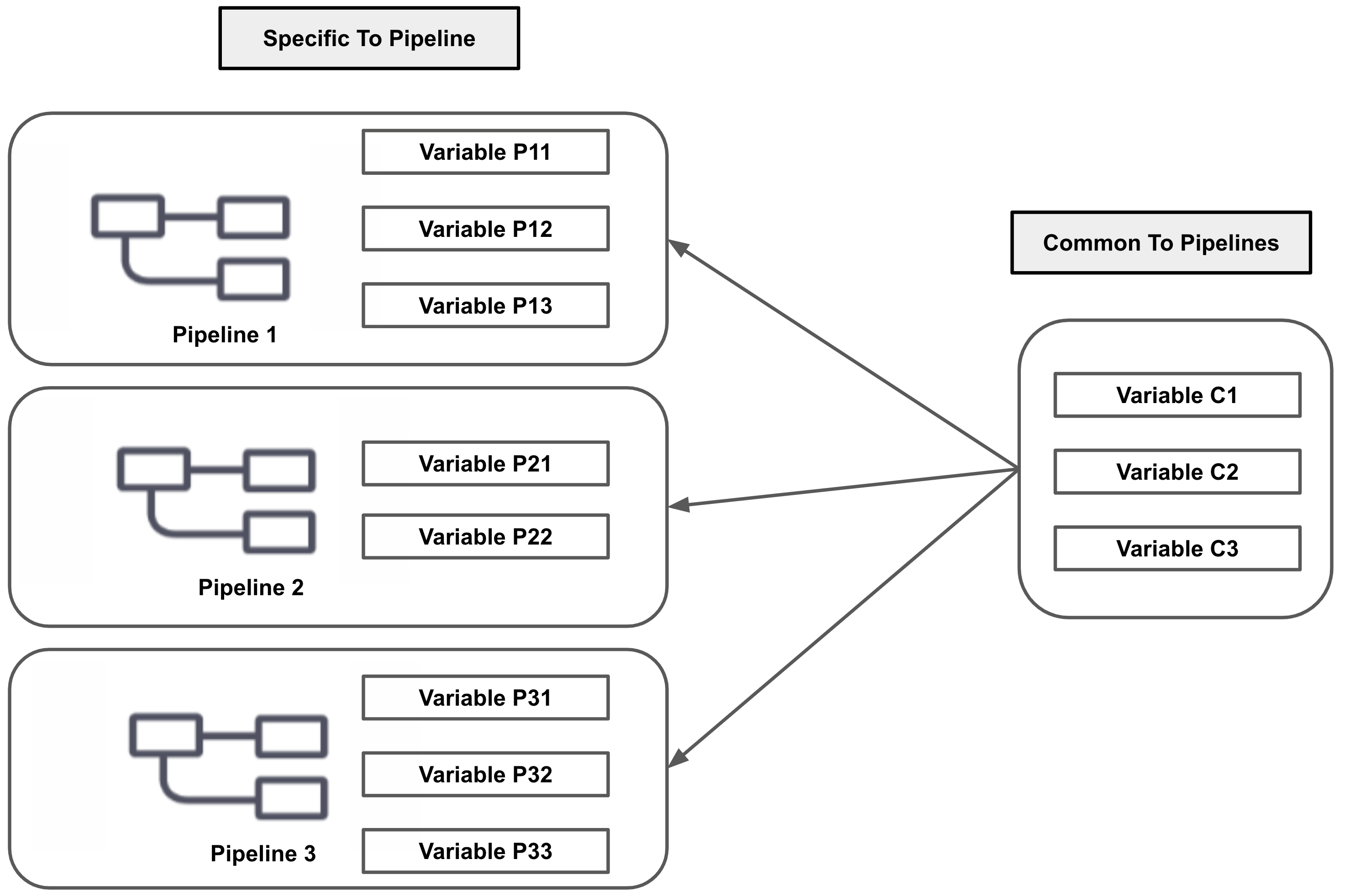
Step 1: Add Account, Org, and Project Variables
You can add a Variable to the Account, Organization, or Project scope.
Account
In Harness, click Account Settings.
Click Account Resources and then click Variables.
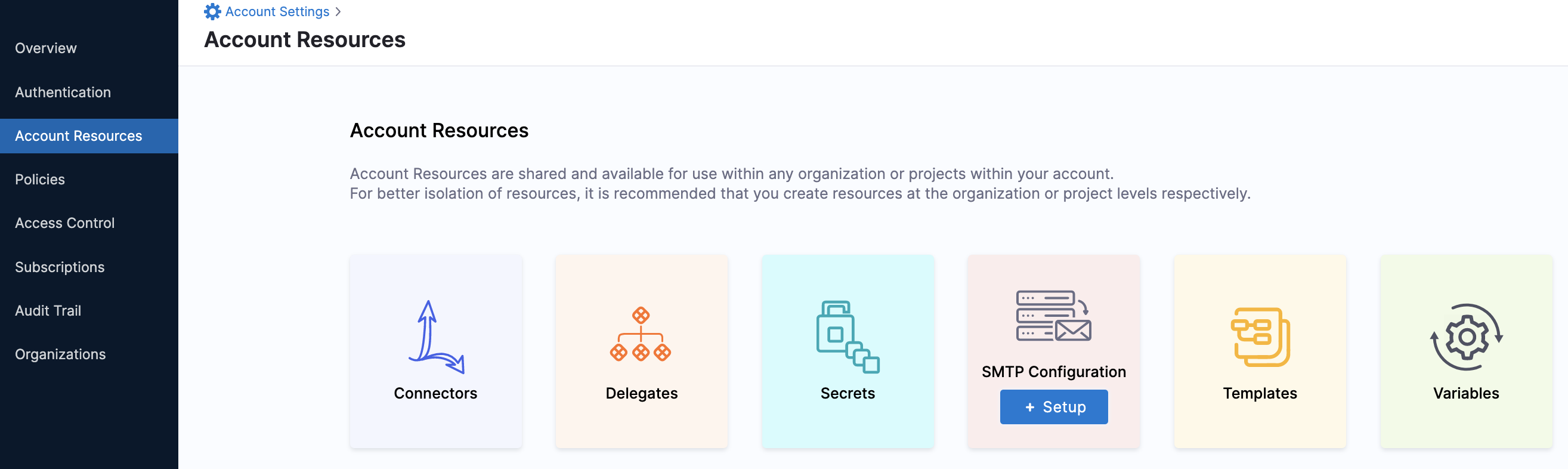
Click New Variable. The Add Variable settings appear.
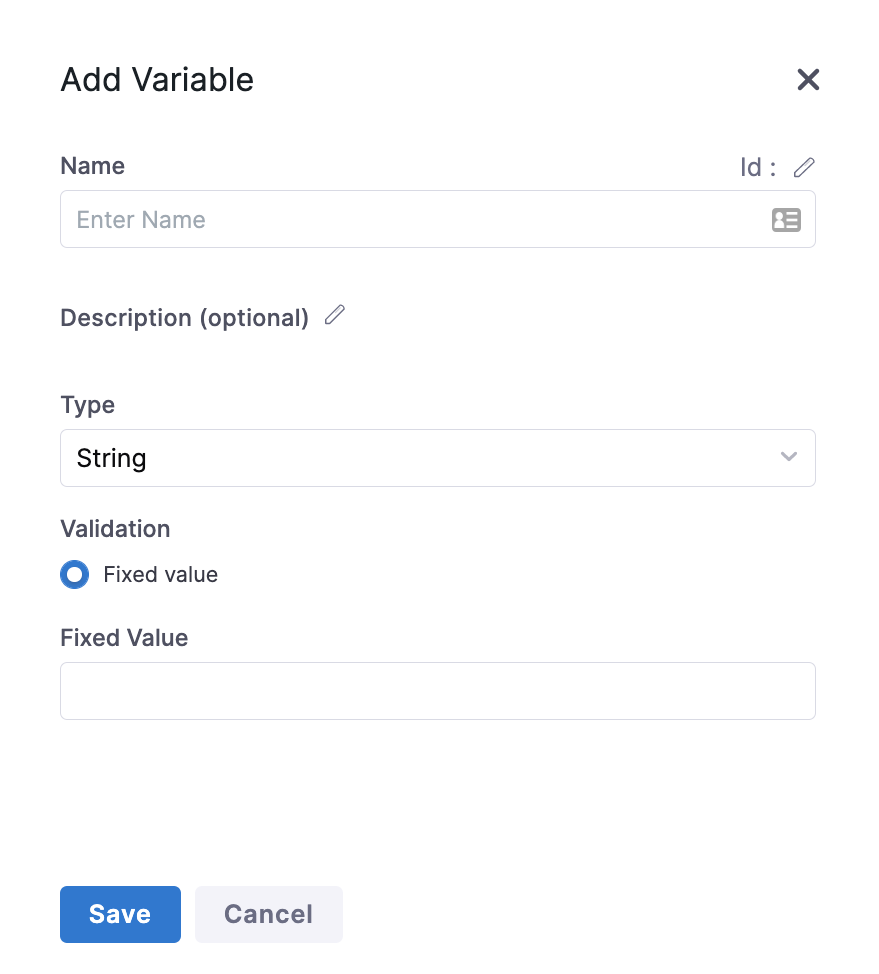
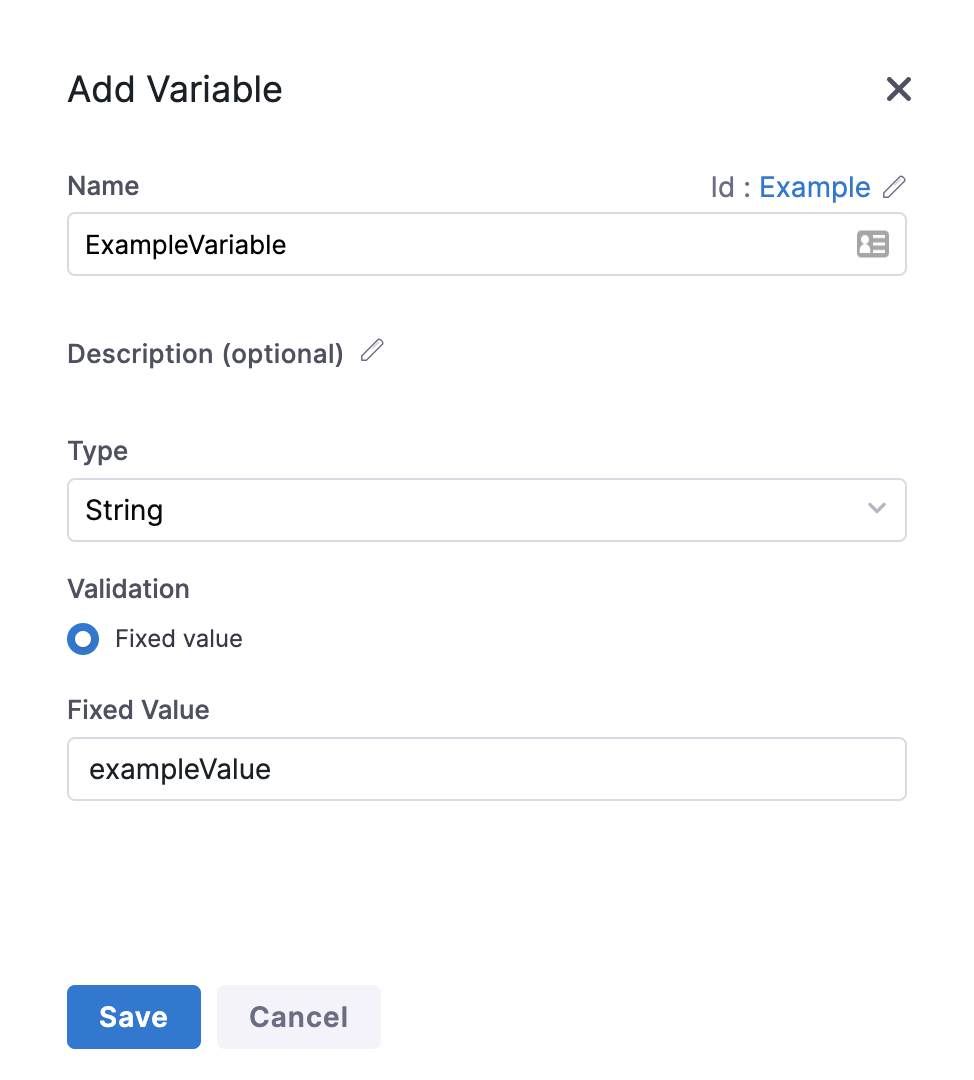
Enter a Name for your Variable.
In Fixed Value, enter a value for your Variable.
Click Save.
Org
Click Account Settings.
Click Organizations.
Select an Org.
In Organization Resources, click Variables.
Click New Variable.
Enter a name, select the variable type (for example, String), and enter a value.
For example, here's a variable named organiz_var.
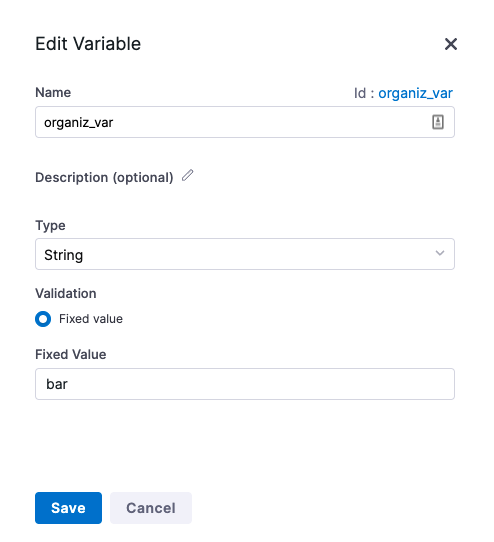
Note the Id. That Id is used to reference the variable.
Click Save.
Project
In a Harness Project, click Project Setup, and then click Variables.
Click New Variable.
Enter a name, select the variable type (for example, String), and enter a value.
For example, here's a variable named proj_var.
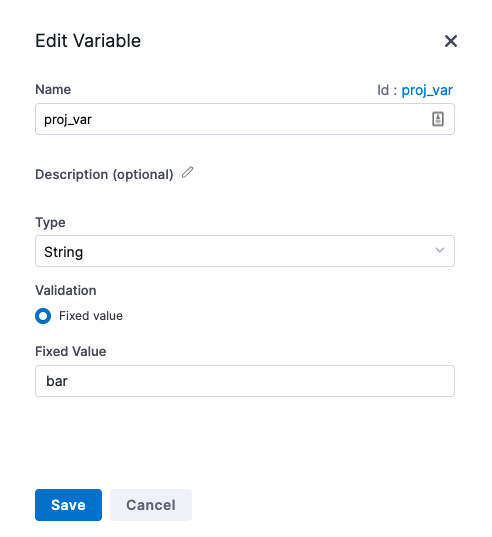
Note the Id. That Id is used to reference the variable.
Click Save.
Step 2: Reference Variables in a Pipeline
To reference an Account and Org-level Variable, you must use the following expression in your Pipeline:
<+variable.[scope].[variable_id]>
- Account-level reference:
<+variable.account.[var Id]> - Org-level reference:
<+variable.org.[var Id]> - Project-level reference:
<+variable.[var Id]>
The expression to reference Project scope Variables is <+variable.Example>. You do not need to specify scope to reference Project Variables.
For example, to reference the Variable you just created, the expression will be:
<+variable.account.Example>
Let us add the Variable in a Pipeline now.
In Harness go to a Pipeline in the same Org as the variable you created.
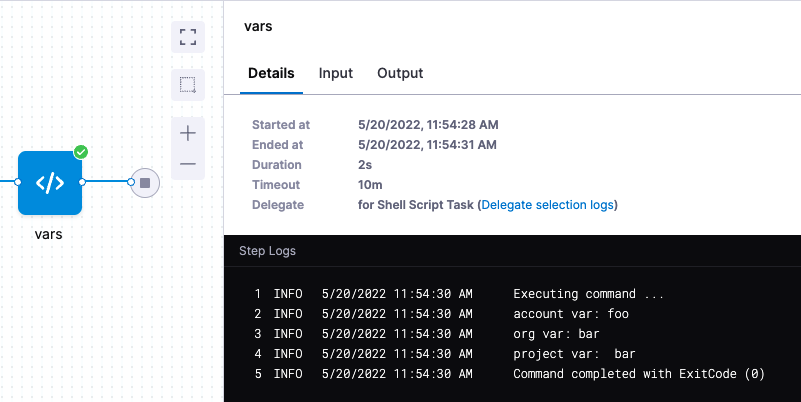
In Execution, add a Shell Script step and reference the variables:
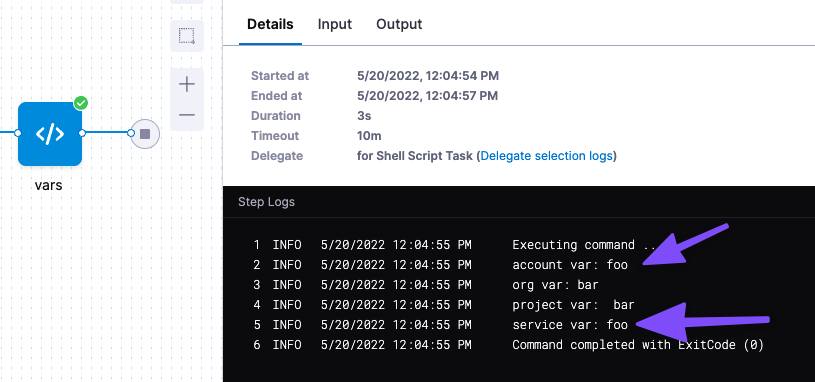
echo "account var: "<+variable.account.acct_var>
echo "org var: "<+variable.org.organiz_var>
echo "project var: " <+variable.proj_var>
When you run the Pipeline, the variable references are resolved and output:
Review: Using an Account, Org, or Project Variable in a Service Variable
In Service, in Advanced, click Add Variable.
The Add Variable settings appear.
In Variable Name, enter a name for your Variable.
Select String as Type and click Save.
Your Variable is now listed under Variables.
In VALUE, select Expression and enter <+variable.account.acct_var>.
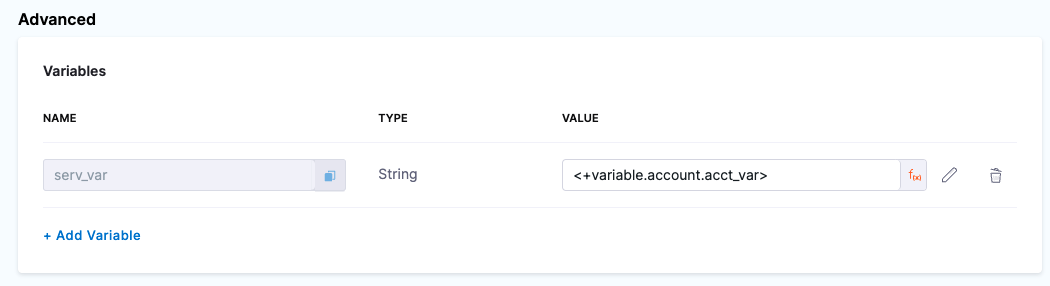
Now, when you run your Pipeline the referenced value is evaluated at runtime.
Copy the Service variable from Variables:
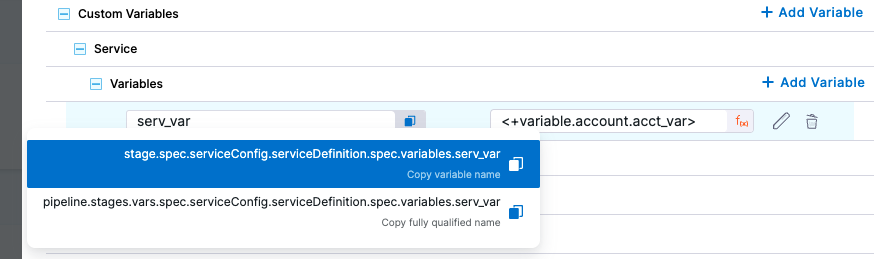
In your Shell Script step, reference the Service variable with <+stage.spec.serviceConfig.serviceDefinition.spec.variables.serv_var>.
Run the Pipeline and see that the value for the Account Variable is passed into the Service Variable:
You can refer to a Variable in most settings. For example, if you an Account Variable storing a Service named Example, you can refer to it inline using the same expression.
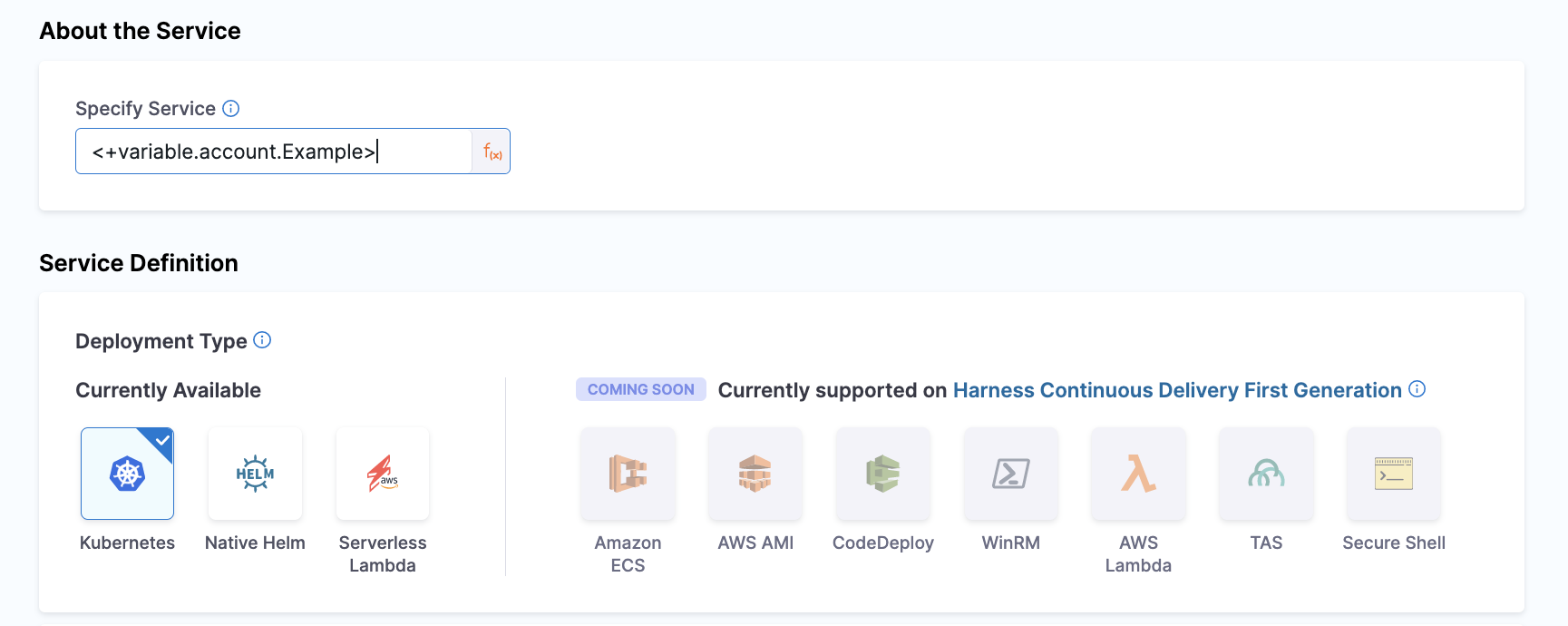
Now, when you run your Pipeline the referenced value is evaluated at runtime.