CI Run step settings
You can use a CI Run step to run scripts in CI Build stages. This topic describes settings for the Run step.
Depending on the stage's build infrastructure, some settings may be unavailable or optional.
Name
Enter a name summarizing the step's purpose. Harness automatically assigns an Id (Entity Identifier Reference) based on the Name. You can change the Id.
Description
Optional text string describing the step's purpose.
Container Registry and Image
The Container Registry is a Harness container registry connector for the image that you want Harness to run build commands on, such as Docker Hub.
The Image is the FQN (fully-qualified name) or artifact name of the Docker image to use when this step runs commands, for example us.gcr.io/playground-123/quickstart-image. The image name should include the tag. If you don't include a tag, Harness uses the latest tag.
You can use any Docker image from any Docker registry, including Docker images from private registries. Different container registries require different name formats:
Docker Registry: Input the name of the artifact you want to deploy, such as
library/tomcat. Wildcards aren't supported. FQN is required for images in private container registries.ECR: Input the FQN (fully-qualified name) of the artifact you want to deploy. Images in repos must reference a path, for example:
40000005317.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/todolist:0.2.GCR: Input the FQN (fully-qualified name) of the artifact you want to deploy. Images in repos must reference a path starting with the project ID that the artifact is in, for example:
us.gcr.io/playground-243019/quickstart-image:latest.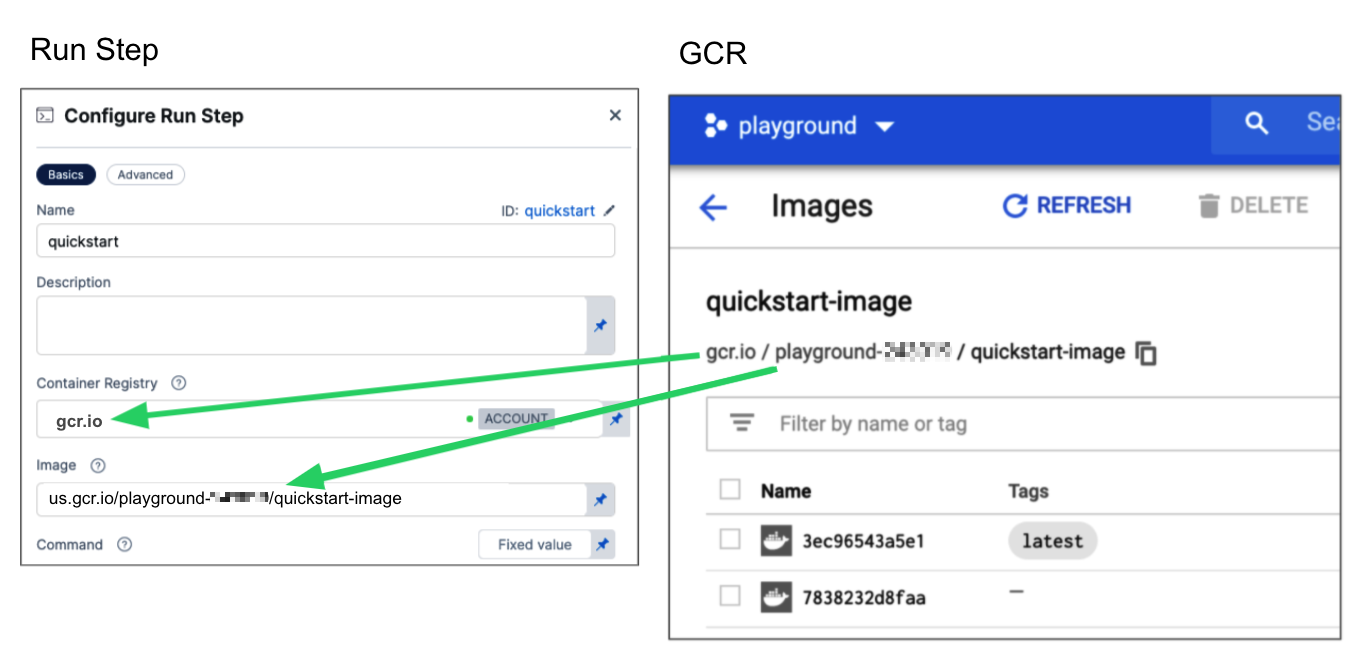
The stage's build infrastructure determines whether these fields are required or optional:
- Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure: Container Registry and Image are always required.
- Local runner build infrastructure: Container Registry and Image are always required.
- Self-hosted cloud provider VM build infrastructure: Run steps can use binaries that you've made available on your build VMs. The Container Registry and Image are required if the VM doesn't have the necessary binaries. These fields are located under Optional Configuration for stages that use self-hosted VM build infrastructure.
- Harness Cloud build infrastructure: Run steps can use binaries available on Harness Cloud machines, as described in the image specifications. The Container Registry and Image are required if the machine doesn't have the binary you need. These fields are located under Optional Configuration for stages that use Harness Cloud build infrastructure.
Shell and Command
Use these fields to define the commands that you need to run in this step.
For Shell, select the shell script type. Options include: Bash, Powershell, Pwsh, Sh, and Python. If the step includes commands that aren't supported for the selected shell type, the build fails. Required binaries must be available on the build infrastructure or the specified image, as described in Container Registry and Image.
In the Command field, enter POSIX shell script commands for this step. The script is invoked as if it were the entry point. If the step runs in a container, the commands are executed inside the container.
You can reference services started in Background steps by using the Background step's Id in your Run step's Command. For example, a curl command could call [backgroundStepId]:5000 where it might otherwise call localhost:5000.
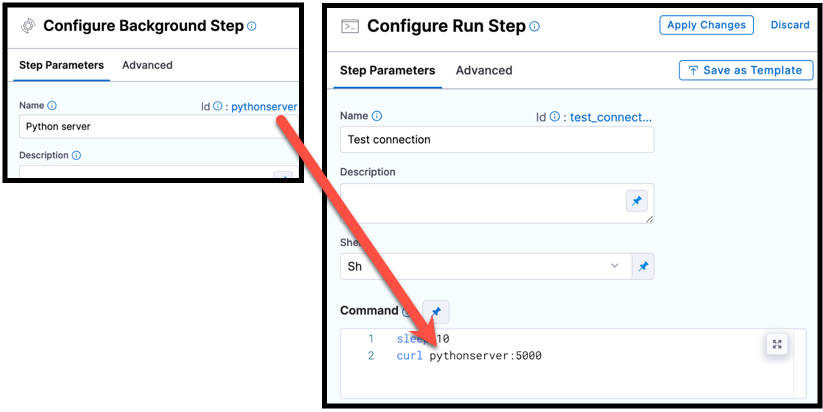
Select each tab below to view examples for each shell type.
- Bash
- Powershell
- Pwsh
- Sh
- Python
This Bash script example checks the Java version.
- step:
...
spec:
shell: Bash
command: |-
JAVA_VER=$(java -version 2>&1 | head -1 | cut -d'"' -f2 | sed '/^1\./s///' | cut -d'.' -f1)
if [[ $JAVA_VER == 17 ]]; then
echo successfully installed $JAVA_VER
else
exit 1
fi
This is a simple Powershell Wait-Event example.
- step:
...
spec:
shell: Powershell
command: Wait-Event -SourceIdentifier "ProcessStarted"
You can run Powershell commands on Windows VMs running in AWS build farms.
This Powershell Core example runs ForEach-Object over a list of events.
- step:
...
spec:
shell: Pwsh
command: |-
$Events = Get-EventLog -LogName System -Newest 1000
$events | ForEach-Object -Begin {Get-Date} -Process {Out-File -FilePath Events.txt -Append -InputObject $_.Message} -End {Get-Date}
You can run Powershell Core commands in pods or containers that have pwsh installed.
In this example, the pulls a python image and executes a shell script (Sh) that runs pytest with code coverage.
- step:
...
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
image: python:latest
shell: Sh
command: |-
echo "Welcome to Harness CI"
uname -a
pip install pytest
pip install pytest-cov
pip install -r requirements.txt
pytest -v --cov --junitxml="result.xml" test_api.py test_api_2.py test_api_3.py
If the shell is Python, supply Python commands directly in command.
This example uses a basic print command.
steps:
- step:
...
spec:
shell: Python
command: print('Hello, world!')
If your script produces an output variable, you must declare the output variable in the Run step's Output Variables. For example, the following step runs a python script that defines an output variable called OS_VAR, and OS_VAR is also declared in the outputVariables.
- step:
type: Run
name: Run_2
identifier: Run_2
spec:
shell: Python
command: |-
import os
os.environ["OS_VAR"] = value
outputVariables:
- name: OS_VAR
Optional Configuration
Use the following settings to add additional configuration to the step. Settings specific to containers, such as Set Container Resources, are not applicable when using the step in a stage with VM or Harness Cloud build infrastructure.
Privileged
Enable this option to run the container with escalated privileges. This is equivalent to running a container with the Docker --privileged flag.
Report Paths
The path to the file(s) that store test results in the JUnit XML format. You can add multiple paths. If you specify multiple paths, make sure the files contain unique tests to avoid duplicates. Glob is supported.
This setting is required for the Run step to be able to publish test results.
Environment Variables
You can inject environment variables into a container and use them in the Command script. You must input a Name and Value for each variable.
You can reference environment variables in the Command script by their name. For example, a Bash script would use $var_name or ${var_name}, and a Windows PowerShell script would use $Env:varName.
Variable values can be Fixed Values, Runtime Inputs, and Expressions. For example, if the value type is expression, you can input a value that references the value of some other setting in the stage or pipeline. Select the Thumbtack to change the value type.
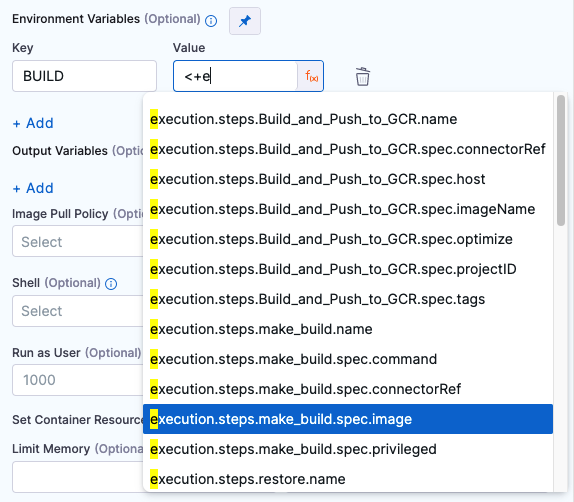
For more information, go to the Built-in Harness Variables Reference.
Output Variables
Output variables expose values for use by other steps or stages in the pipeline.
To create an output variable, do the following in the step where the output variable originates:
In the Command field, export the output variable. For example, the following command exports a variable called
myVarwith a value ofvarValue:export myVar=varValueIn the step's Output Variables, declare the variable name, such as
myVar.
To call a previously-exported output variable in a later step or stage in the same pipeline, use a variable expression that includes the originating step's ID and the variable name.
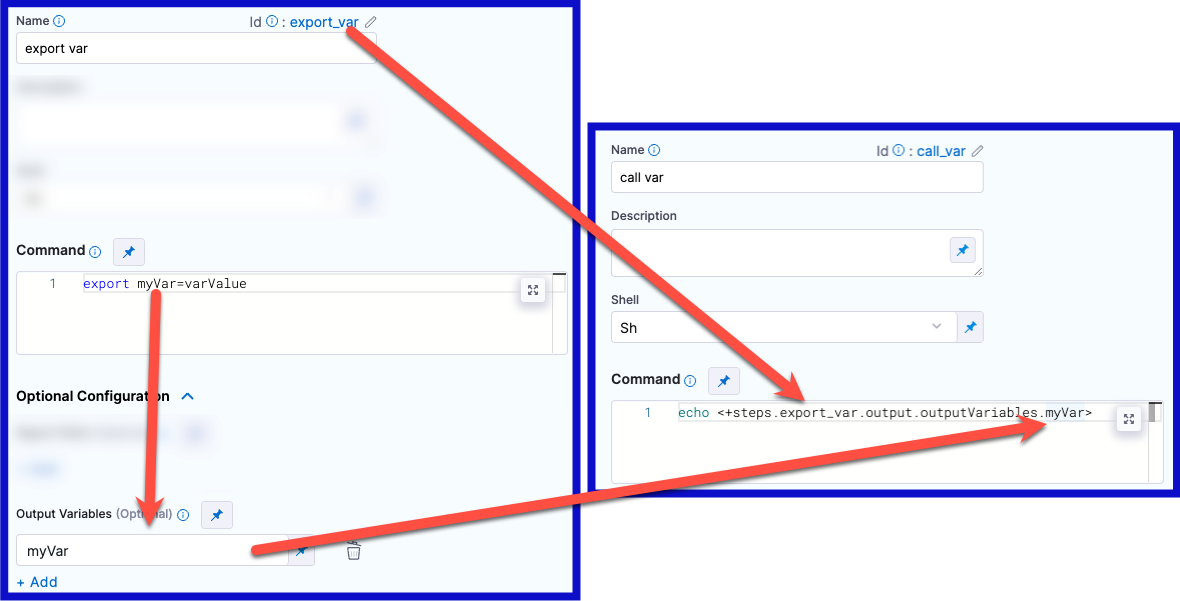
To reference an output variable in another step in the same stage, use either of the following expressions:
<+steps.[stepID].output.outputVariables.[varName]>
<+execution.steps.[stepID].output.outputVariables.[varName]>
To reference an output variable in a different stage than the one where it originated, use either of the following expressions:
<+stages.[stageID].spec.execution.steps.[stepID].output.outputVariables.[varName]>
<+pipeline.stages.[stageID].spec.execution.steps.[stepID].output.outputVariables.[varName]>
YAML example: Output variable
In the following YAML example, step alpha exports an output variable called myVar, and then step beta references that output variable.
- step:
type: Run
name: alpha
identifier: alpha
spec:
shell: Sh
command: export myVar=varValue
outputVariables:
- name: myVar
- step:
type: Run
name: beta
identifier: beta
spec:
shell: Sh
command: |-
echo <+steps.alpha.output.outputVariables.myVar>
echo <+execution.steps.alpha.output.outputVariables.myVar>
Image Pull Policy
If you specified a Container Registry and Image, you can specify an image pull policy:
- Always: The kubelet queries the container image registry to resolve the name to an image digest every time the kubelet launches a container. If the kubelet encounters an exact digest cached locally, it uses its cached image; otherwise, the kubelet downloads (pulls) the image with the resolved digest, and uses that image to launch the container.
- If Not Present: The image is pulled only if it is not already present locally.
- Never: The image is assumed to exist locally. No attempt is made to pull the image.
Run as User
If you specified a Container Registry and Image, you can specify the user ID to use for running processes in containerized steps.
For a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure, the step uses this user ID to run all processes in the pod. For more information, go to Set the security context for a pod.
Set Container Resources
Maximum resources limits for the resources used by the container at runtime:
- Limit Memory: Maximum memory that the container can use. You can express memory as a plain integer or as a fixed-point number with the suffixes
GorM. You can also use the power-of-two equivalents,GiorMi. Do not include spaces when entering a fixed value. The default is500Mi. - Limit CPU: The maximum number of cores that the container can use. CPU limits are measured in CPU units. Fractional requests are allowed. For example, you can specify one hundred millicpu as
0.1or100m. The default is400m. For more information, go to Resource units in Kubernetes.
Timeout
Set the timeout limit for the step. Once the timeout limit is reached, the step fails and pipeline execution continues. To set skip conditions or failure handling for steps, go to: