Set up a GCP VM build infrastructure
Currently, this feature is behind the Feature Flag CI_VM_INFRASTRUCTURE. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
This topic describes how to set up a CI build infrastructure in Google Cloud Platform. You will create an Ubuntu VM and then install a CI Delegate and Drone Runner on it. The Delegate creates VMs dynamically in response to CI build requests.
For information on using Kubernetes as a build farm, see Set up a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure.
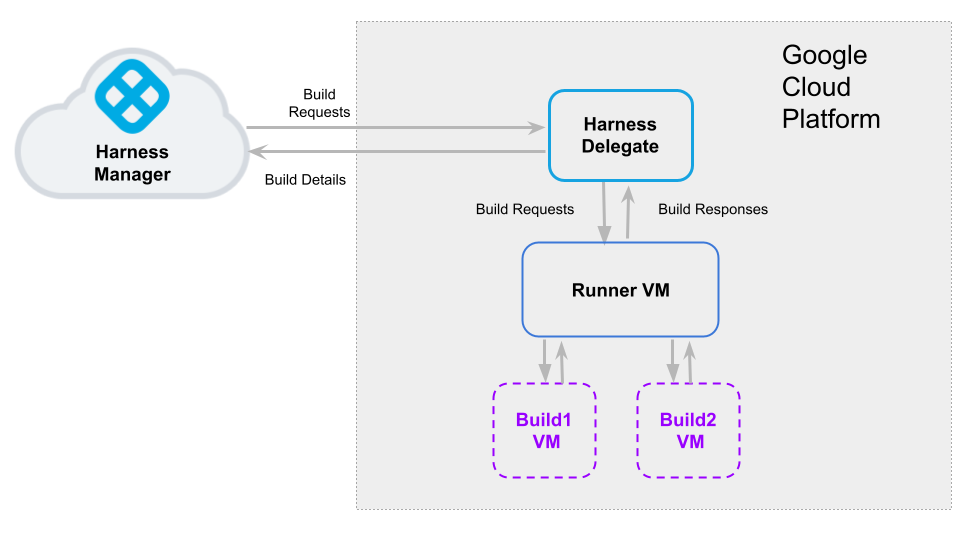
The following diagram illustrates a build farm. The Harness Delegate communicates directly with your Harness instance. The VM Runner maintains a pool of VMs for running builds. When the Delegate receives a build request, it forwards the request to the Runner, which runs the build on an available VM.
Important Notes
- Google Cloud VM configuration:
- For the delegate VM, use a machine type with 4 vCPU and 16 GB memory or more.
- Harness recommends the Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic) machine image.
- The VM must allow ingress access on ports 22 and 9079.
To find images to use on Google Compute Engine, use the following command:
gcloud compute images list
A valid image reference looks like this: projects/{PROJECT}/global/images/{IMAGE}
For example: projects/docs-test/global/images/ubuntu-pro-1804-bionic-v20220131
Step 1: Set up the delegate VM
Log into the Google Cloud Console and launch the VM that will host your Harness delegate.
Install Docker on the VM.
Install Docker Compose on the VM. You must have Docker Compose version 3.7 or higher installed.
Run this command on the VM:
gcloud auth application-default loginThis creates the following credentials file:
/home/$(whoami)/.config/gcloud/application_default_credentials.jsonCreate a
/runnerfolder on your VM andcdinto it:mkdir /runner
cd /runner
Step 2: Configure the Drone pool on the Google VM
The pool.yml file defines the VM spec and pool size for the VM instances used to run the pipeline. A pool is a group of instantiated VMs that are immediately available to run CI pipelines.
- In the
/runnerfolder, create a newpool.ymlfile. - Set up the file as described in the following example. Note the following:
- To avoid latency issues between delegate and build VMs, specify the same zone where your delegate is running in the
spec: zone:field. - Set up
spec: account:with your Google project ID and your JSON credentials file. - For information about specific settings, go to the Pool Settings Reference. You can also learn more in the Drone documentation for Drone Pool and Google.
- To avoid latency issues between delegate and build VMs, specify the same zone where your delegate is running in the
Example pool.yml
version: "1"
instances:
- name: ubuntu-gcp
default: true
type: google
pool: 1
limit: 1
platform:
os: linux
arch: amd64
spec:
account:
project_id: ci-play
json_path: /path/to/key.json
image: projects/ubuntu-os-pro-cloud/global/images/ubuntu-pro-1804-bionic-v20220510
machine_type: e2-small
zone:
- us-centra1-a
- us-central1-b
- us-central1-c
disk:
size: 100
type: "pd-balanced"
Later in this workflow, you'll reference the pool identifier in Harness Manager to map the pool with a Stage Infrastructure in a CI Pipeline. This is described later in this topic.
Step 3: Configure the docker-compose.yaml file
- In your Harness account, organization, or project, select Delegates under Project Setup.
- Click New Delegate and select Switch back to old delegate install experience.
- Select Docker and then select Continue.
- Enter a Delegate Name. Optionally, you can add Tags or Delegate Tokens. Then, select Continue.
- Select Download YAML file to download the
docker-compose.yamlfile to your local machine.
Next, you'll add the Runner spec to the new Delegate definition. The Harness Delegate and Runner run on the same VM. The Runner communicates with the Harness Delegate on localhost and port 3000 of your VM.
Copy your local
docker-compose.yamlfile to the/runnerfolder on the VM. This folder should now have bothdocker-compose.yamlandpool.yml.Open
docker-compose.yamlin a text editor.Append the following to the end of the
docker-compose.yamlfile:drone-runner-aws:
restart: unless-stopped
image: drone/drone-runner-aws:latest
volumes:
- /runner:/runner
- /path/to/google/credentials/file/:/key
# example: /home/jsmith/.config/gcloud/:/key
entrypoint: ["/bin/drone-runner-aws", "delegate", "--pool", "pool.yml"]
working_dir: /runner
ports:
- "3000:3000"Under
services: harness-ng-delegate: restart: unless-stopped, add the following line:network_mode: "host"Save
docker-compose.yaml.
Example: docker-compose.yaml with Runner spec
version: "3.7"
services:
harness-ng-delegate:
restart: unless-stopped
network_mode: "host"
deploy:
resources:
limits:
cpus: "0.5"
memory: 2048M
image: harness/delegate:latest
environment:
- ACCOUNT_ID=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
- ACCOUNT_SECRET=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
- MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT=https://app.harness.io
- WATCHER_STORAGE_URL=https://app.harness.io/public/qa/premium/watchers
- WATCHER_CHECK_LOCATION=current.version
- REMOTE_WATCHER_URL_CDN=https://app.harness.io/public/shared/watchers/builds
- DELEGATE_STORAGE_URL=https://app.harness.io
- DELEGATE_CHECK_LOCATION=delegateqa.txt
- USE_CDN=true
- CDN_URL=https://app.harness.io
- DEPLOY_MODE=KUBERNETES
- DELEGATE_NAME=qwerty
- NEXT_GEN=true
- DELEGATE_DESCRIPTION=
- DELEGATE_TYPE=DOCKER
- DELEGATE_TAGS=
- DELEGATE_TASK_LIMIT=50
- DELEGATE_ORG_IDENTIFIER=
- DELEGATE_PROJECT_IDENTIFIER=
- PROXY_MANAGER=true
- VERSION_CHECK_DISABLED=false
- INIT_SCRIPT=echo "Docker delegate init script executed."
drone-runner-aws:
restart: unless-stopped
image: drone/drone-runner-aws:latest
volumes:
- /runner:/runner
- /home/jsmith/.config/gcloud/:/key
entrypoint: ["/bin/drone-runner-aws", "delegate", "--pool", "pool.yml"]
working_dir: /runner
ports:
- "3000:3000"
For more information on Harness Docker Delegate environment variables, go to the Harness Docker Delegate environment variables reference.
Step 4: Install the Delegate and Runner
SSH into the Delegate VM and
cdto/runner.Confirm that the folder has both setup files, for example:
$ ls -a
. .. docker-compose.yml pool.ymlRun the following command to install the Delegate and Runner:
$ docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml up -dVerify that both containers are running correctly. You might need to wait a few minutes for both processes to start. You can run the following commands to check the process status:
$ docker ps
$ docker logs <delegate-container-id>
$ docker logs <runner-container-id>In the Harness UI, verify that the Delegate appears in the Delegates list. It might take two or three minutes for the Delegates list to update. Make sure the Connectivity Status is Connected. If the Connectivity Status is Not Connected, make sure the Docker host can connect to
https://app.harness.io.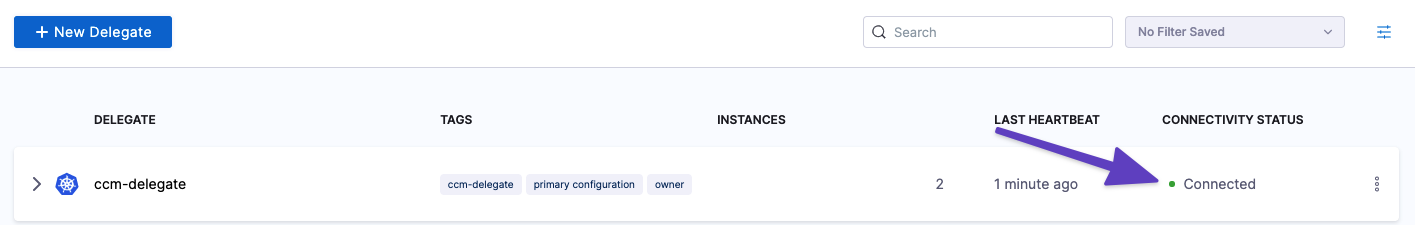
The Delegate and Runner are now installed, registered, and connected.
Step 5: Select pipeline build infrastructure
In your CI pipeline's Build stage, select the Infrastructure tab, and then select VMs.
In the Pool ID, enter the pool
namefrom your pool.yml.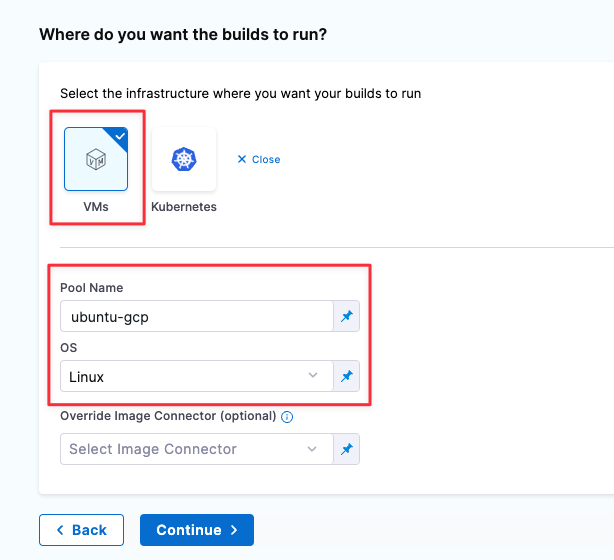
This pipeline's Build stage now uses your GCP VMs for its build infrastructure.
Pool Settings Reference
You can configure the following settings in your pool.yml file.
| Subfields | Examples | Description |
name (String) | NA | name: windows_pool |
pool (Integer) | NA | pool: 1 |
limit (Integer) | NA | limit: 3 |
platform | os (String) | platform: os: windowsarch (String) |
spec | Configure the settings of your build VMs as described in Build VM Settings. |
Build VM Settings
account: Specify your GCP project Id and the full path and filename of your local Google credentials file.image: The image type to use for the build VM.machine_type: The google machine type. See About Machine Families in the Google Cloud docs.zone: To minimize latency, specify the zone where the Delegate is running.
Troubleshooting (Advanced)
If you have problems running the delegate, runner, or VMs, you can collect debug and trace information in your container logs.
- Create a
.envfile with the following options in your/runnerfolder:DRONE_DEBUG=true
DRONE_TRACE=true - Shut down the delegate and runner:
docker-compose down - In your
docker-compose.ymlfile, update thedrone-runner-aws: entrypointto include the.envfile:drone-runner-aws:
restart: unless-stopped
image: drone/drone-runner-aws:1.0.0-rc.9
volumes:
- /runner:/runner
- /home/jsmith/.config/gcloud/:/key
entrypoint: ["/bin/drone-runner-aws", "delegate", "--envfile", ".env", "--pool", "pool.yml"]
working_dir: /runner
ports:
- "3000:3000" - Restart the delegate and runner:
docker-compose up
See Also
- Set up a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure
- For more details on VM Runner, go to this GitHub page.