Early access features
Review the notes below to learn about the early access (aka BETA) features in Harness NextGen SaaS across all Harness modules and the Harness Platform. Early access features require a feature flag. For FirstGen release notes, go to Harness SaaS Release Notes (FirstGen).
Harness deploys changes to Harness SaaS clusters on a progressive basis. This means that the features described in these release notes may not be immediately available in your cluster. To identify the cluster that hosts your account, go to the Account Overview page.
Latest - May 04, 2023, version 79214
Continuous Delivery
You can set webhook triggers to run specific pipeline stages using the Allow selective stage(s) executions? option. (CDS-56775, CDS-56774)
This functionality is behind the feature flag,
CDS_NG_TRIGGER_SELECTIVE_STAGE_EXECUTION.To run a particular stage of the pipeline:
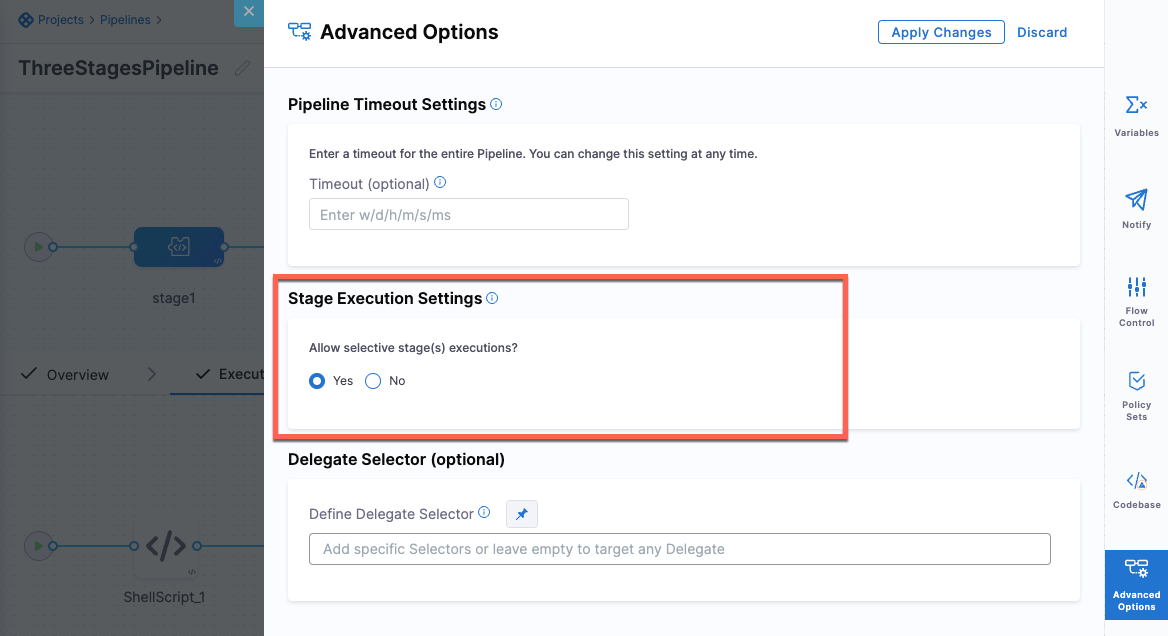
Select the stage, then select Advanced Options.
In Stage Execution Settings> Allow selective stages(s) executions?, select Yes. This setting is selected by default.
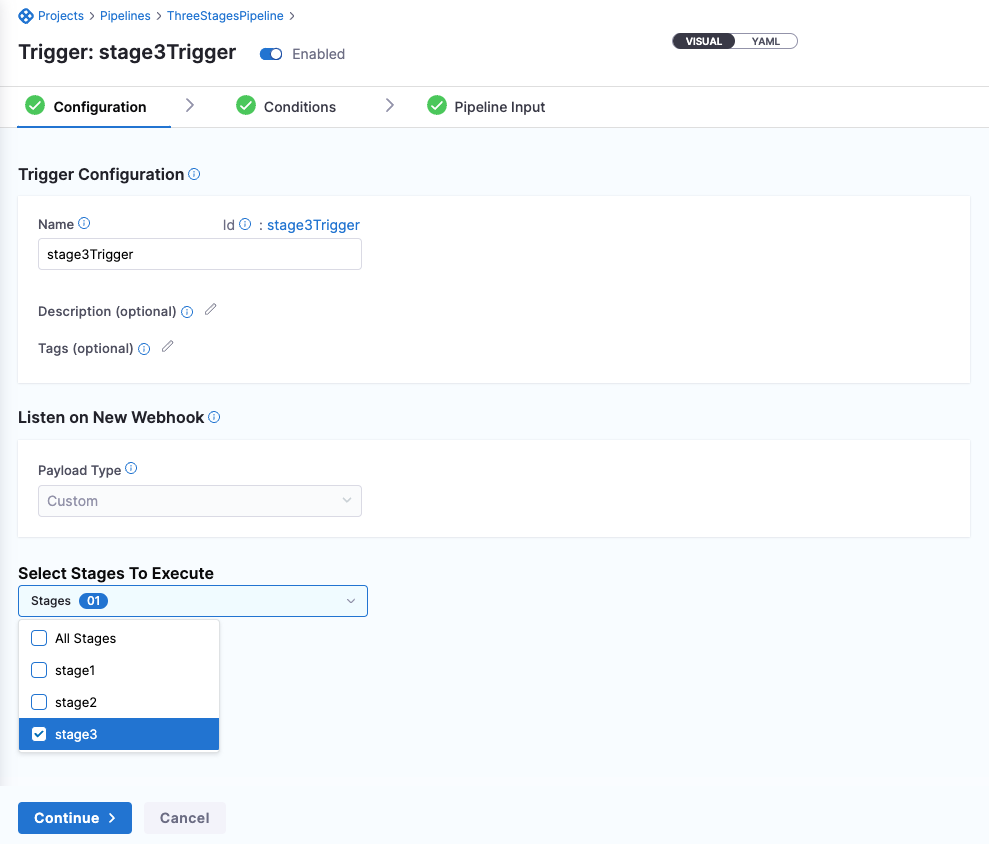
When you create a trigger, in Configuration, select the stages you want to execute.
Here is a sample trigger YAML:
trigger:
name: stage3Trigger
identifier: stage3Trigger
enabled: true
description: ""
tags: {}
stagesToExecute:
- stage3
orgIdentifier: NgTriggersOrg
projectIdentifier: viniciusTest
pipelineIdentifier: ThreeStagesPipeline
source:
type: Webhook
spec:
type: Custom
spec:
payloadConditions: []
headerConditions: []
inputYaml: |
pipeline:
identifier: ThreeStagesPipeline
stages:
- stage:
identifier: stage3
type: Custom
variables:
- name: stage3var
type: String
value: stage3VarYou can add Tanzu Application Service (TAS) config files from GitHub. (CDS-56452)
This feature is currently behind the feature flag,
CDS_GIT_CONFIG_FILES. For TAS deployment types, you can reference service config files from GitHub.
Previous releases
2023 releases
April 21, 2023, version 79111
Continuous Delivery
Protecting secrets used in webhook-based triggers that use secret decryption on delegates (CDS-58488, ZD-42117)
This functionality is behind a feature flag,
CDS_NG_TRIGGER_AUTHENTICATION_WITH_DELEGATE_SELECTOR.Github triggers that use a secret for authentication will now use the same delegate selectors saved in the secret's Harness secret manager.
Harness now supports variable expressions in the plain text config files. (CDS-58399)
This functionality is behind a feature flag,
CDS_NG_CONFIG_FILE_EXPRESSION.Variable expression support includes service, environment, pipeline, and stage variables. Any Harness expression is supported.
Variable expressions are not supported for encrypted text config files because expressions impact the encoded secret.
Config files can now be pulled from Github. (CDS-56652)
This functionality is behind a feature flag,
CDS_GIT_CONFIG_FILES.For Harness services using the Tanzu deployment type, config files can be configured using Github, in addition to the Harness file store. Support for other deployment types in coming soon.
April 10, 2023, version 79015
Continuous Delivery
This functionality is behind a feature flag,
CDS_AWS_NATIVE_LAMBDA.Harness supports the deployment of AWS Lambda functions.
ServiceNow custom table support. (CDS-55046)
This functionality is behind a feature flag,
CDS_SERVICENOW_TICKET_TYPE_V2.Custom table support is now available in Harness' ServiceNow integration.
Harness recommends that you only use a table extending task, or extend tables that indirectly extend the task. You can specify any custom table in Harness.
What is a table extending task?
In ServiceNow, a table extending task is a task that involves creating a new table by extending an existing table. When a table is extended, a new child table is created that inherits all the fields, relationships, and other attributes of the parent table. The child table can then be customized further to meet the specific needs of the organization.
Itil roles are not mandatory for using these steps. When using the normal flow for custom tables, you should have sufficient permissions on the custom table, such as basic CRUD permissions, permissions to update desired fields, etc.
When using template flow, your user role is required along with cross scope privileges to the custom table.
The store app is only certified to be used with Incident, Problem, Change Request, and Change Task tables by the ServiceNow certification team.
The custom table being used should allow access to this table via web services.
Harness will remove comments when evaluating commented lines in manifests to avoid rendering failures. (CDS-57721, ZD-41676)
This functionality is behind a feature flag,
CDS_REMOVE_COMMENTS_FROM_VALUES_YAML.Expressions in comments were causing issues for some customers as Harness was trying to evaluate the expressions and this was causing failures.
Harness will remove comments from values.yaml files to prevent expressions in comments from being evaluated and causing failures.
March 24, 2023, version 78817
Harness Platform
By enabling the feature flag,
PL_NEW_SCIM_STANDARDS, any CRUD operation on a user now returns the details of the user groups that the user is part of. (PL-31496)You can use this to verify what groups a given user belongs to.
March 15, 2023, version 78712
Continuous Delivery
Large repositories are now supported for Azure Repo. This functionality is behind a feature flag,
OPTIMIZED_GIT_FETCH_FILES.Harness performs a
git cloneto fetch files. When fetching very large repositories, the network connection may time out. Enable the feature flag,OPTIMIZED_GIT_FETCH_FILESto fetch very large repositories from Azure Repo. When this feature flag is enabled, Harness will use provider-specific APIs to improve performance.
Harness Platform
Harness now populates
givenNameandfamilyNamefor users via SCIM and returns the same when a GET, CREATE, or UPDATE request is made. (PL-31498)This is behind the feature flag
PL_NEW_SCIM_STANDARDS.The response of a CRUD operation on a user or user group now contains the following meta fields as per the SCIM 2.0 standards:
createdAt
lastUpdated
version
resourceType (PL-31497)
This is behind the feature flag
PL_NEW_SCIM_STANDARDS.
March 2, 2023
Security Testing Orchestration
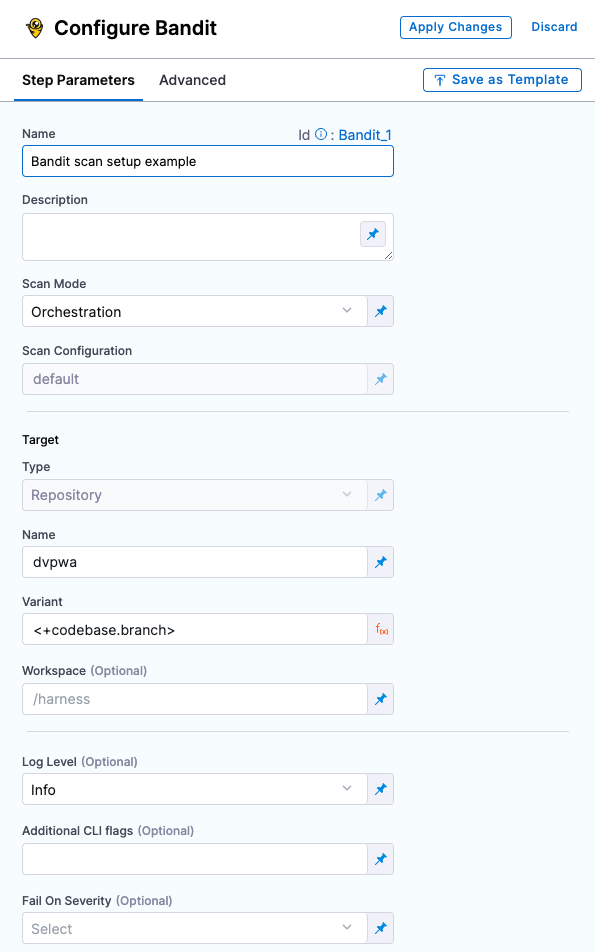
Improved UI for configuring scan steps (STO-4867)
This release includes a set of Security steps with an improved UI for configuring scans. Each step shows only the settings that apply to the specific scan.
Note the following:
- This release includes new steps for the following scanners: Aqua Trivy, Bandit, Black Duck, Checkmarx, Grype, Mend, Prisma Cloud, Snyk, SonarQube, and ZAP.
- Docker-in-Docker is no longer required for these steps unless you're scanning a container image. If you're scanning a repository or running instance, you don't need to set up a Background step running DinD.
- These steps are currently available in Security stages only.
- Support is currently limited to Kubernetes and Harness Cloud AMD64 build infrastructures only.
- For descriptions of all available UI settings, go to Security step UI settings reference.
Security step configuration UI
- This release includes a Jira integration that enables you to create Jira tickets for issues detected during an STO build. For more information, go to Create Jira tickets for detected issues. (STO-5467)
February 15, 2023
Continuous Delivery
Kubernetes Dry Run step added. (CDS-43839)
You can now add the Dry Run step for Kubernetes and Native Helm deployments.
This functionality is behind a feature flag:
K8S_DRY_RUN_NG.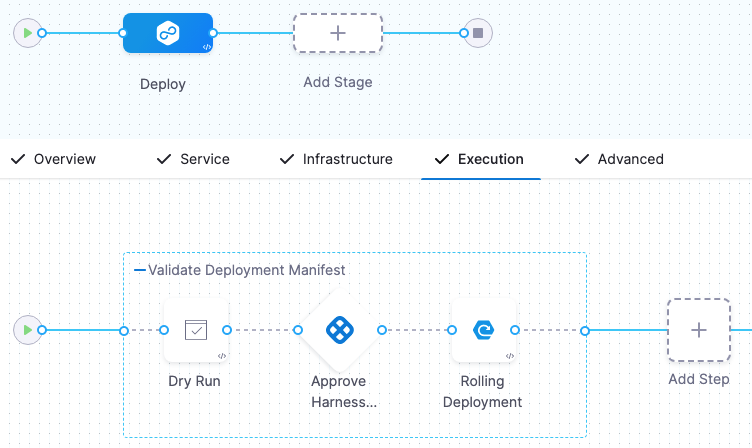
The Dry Run step fetches the Kubernetes manifests or Helm charts in a stage and performs a dry run of those resources. This is the same as running a
kubectl apply --filename=manifests.yaml --dry-run.You can use the Dry Run step to check your manifests before deployment. You can follow the step with an Approval step to ensure the manifests are valid before deployment.
You can reference the resolved manifest from the Dry Run step in subsequent steps using a Harness variable expression.
<+pipeline.stages.[Stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.[Step_Id].k8s.ManifestDryRun>For example, if the stage Id is
Deployand the Dry Run step Id isDry_Runthe expression would be:<+pipeline.stages.Deploy.spec.execution.steps.Dry_Run.k8s.ManifestDryRun>For more information, go to Perform a Kubernetes dry run.
February 6, 2023
Harness Platform
- You can delete a user provisioned in Harness through SCIM in NextGen and retain the user in FirstGen by enabling the feature flag
PL_USER_DELETION_V2. (PL-23577)
January 12, 2023
Continuous Delivery
Convert imperative Kubernetes rollback to declarative rollback. (CDS-2993, ZD-26855, ZD-27690, ZD-36563, ZD-36670)
This functionality is behind a feature flag:
CDP_USE_K8S_DECLARATIVE_ROLLBACK_NG.Harness applies Kubernetes manifest using
kubectl apply, which is a declarative way of creating Kubernetes objects. But when rolling back, we performkubectl rollout undo workloadType/workloadName --to-revision=<REVISION_NUMBER>, which is an imperative way of rolling back. Using imperative and declarative commands together is not recommended and can cause issues.In some instances, the workload spec was not updated properly when
rollout undowas performed. Subsequent deployments then refered to an invalid spec of the workload and caused Kubernetes issues like kubectl rollout undo should warn about undefined behaviour with kubectl apply.What is the fix?
We had to redesign our release history to store all rendered manifests in secrets, just like Helm does. While rolling back, we are now reapplying the last successful release's manifests. This solves this issue.
What is the impact on customers?
- Enabling declarative rollback disables versioning (even if the Skip Versioning checkbox is left unchecked), since versioning was introduced with the imperative rollback design. However, versioning is not needed anymore with declarative rollback.
- The delegate's service account needs the permission to create, update, and read secrets in the defined infrastructure namespace. Typically, customers' delegates already have these permissions, but if cluster roles are strictly scoped, this could cause failures. For information on cluster roles for the delegate, go to Install Harness Delegate on Kubernetes.
2022 releases
December 13, 2022
Service Reliability Management
Continuous Verification (CV) fails if the data for configured deployment strategy is not available (SRM-12731)
Harness was automatically applying an alternate deployment strategy even if the required data for the deployment configured in the Verify step was not available.
Now, Harness does not automatically apply an alternate deployment strategy if the required data is not available. Instead, Harness fails the CV. Harness automatically applies an alternate deployment strategy only if you choose the Auto option in the Continuous Verification Type dropdown list when configuring the Verify step.
This feature is behind the feature flag SRM_LOG_HOST_SAMPLING_ENABLE.
December 7, 2022
Continuous Delivery
Nexus 3 is now supported for Azure Web App artifacts. (CDS-46372)
For more information, see Azure Web Apps deployment tutorial
This functionality is behind a feature flag: AZURE_WEB_APP_NG_NEXUS_PACKAGE
November 29, 2022
Continuous Delivery
Terraform Backend Configuration file path in the Terraform Apply step now supports remote file repos. (CDS-39012, ZD-37065)
Terraform Backend Configuration now can be specified in the remote file repository.
For more details, go to Provision with the Terraform Apply Step.
This functionality is behind a feature flag: TERRAFORM_REMOTE_BACKEND_CONFIG.
November 11, 2022
Harness Platform
You can now create secrets using the Google Cloud Secret Manager in Harness. (PL-28978)
For more information, see Add a Google Cloud Secret Manager
You can now select modules and configure your own navigation in Harness. (SPG-153)
Also, Projects is a new option in the left navigation. Click Projects to view the project-specific overview, pipeline, connector, and other details.
November 6, 2022
Harness Platform
You can now get optimized performance on remote pipelines by enabling the feature flag USE_GET_FILE_V2_GIT_CALL if you are on delegate version 772xx or higher. (PL-29459)
If you are on an older delegate version, you can upgrade your delegate for optimized performance.
October 20, 2022
Feature Flags
We've released a beta version of an Apex SDK for Feature Flags.
For more information and to access this SDK, see the Apex SDK reference guide and the GitHub repository.
October 18, 2022
Continuous Delivery
ECS Run Task support
In addition to deploying tasks as part of your standard ECS deployment, you can use the ECS Run Task step to run individual tasks separately as a step in your ECS stage. The ECS Run Task step is available in all ECS strategy types. An example of when you run a task separately is a one-time or periodic batch job that does not need to keep running or restart when it finishes.
This functionality is behind feature flags: NG_SVC_ENV_REDESIGN and ECS_NG
For more information, go to the ECS tutorial's run task step.
October 7, 2022
Continuous Delivery
- ECS deployments: deploy artifacts to your Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) clusters using a Rolling, Canary, and Blue Green strategies.
Enable Feature Flags NG_SVC_ENV_REDESIGN and ECS_NG.
For more information, go to the ECS deployment tutorial.
- Traditional deployments using SSH or WinRM: deploy your artifacts to hosts located in Microsoft Azure, AWS, or any platform-agnostic Physical Data Center (PDC).
These deployments are called Traditional because they use Secure Shell and PowerShell scripts and a traditional runtime environment as opposed to containers and orchestration mechanisms, like Kubernetes.
Enable Feature Flags NG_SVC_ENV_REDESIGN, SSH_NG, and PIPELINE_MATRIX.
For more information, go to Secure Shell (SSH) deployment tutorial and WinRM deployment tutorial.
- Custom deployments using Deployment templates: In some cases, you might be using a platform that does not have first class support in Harness, such as OpenStack, WebLogic, WebSphere, Google Cloud functions, etc. We call these non-native deployments. For non-native deployments, Harness provides a custom deployment option using Deployment Templates.
Enable Feature Flags NG_SVC_ENV_REDESIGN and NG_DEPLOYMENT_TEMPLATE.
For more information, go to the Custom deployments using deployment templates tutorial.
Harness Platform
- You can now create remote Templates in Harness and save it in your Git repo by enabling the feature flag NG_TEMPLATE_GITX. (PL-28573)
For more information, see Create a remote step template, Create a remote stage template, and Create a remote pipeline template.
- You can now use expressions to reference pre-existing secrets in Vault using a fully-qualified path. (PL-28352)
For more information, see HashiCorp Vault Secrets.
- Harness will now send email notification for user invites when the feature flag AUTO_ACCEPT_SAML_ACCOUNT_INVITES is enabled. (PL-26218, ZD-32152,35287)
Harness will not send any emails for user invites when the feature flag PL_NO_EMAIL_FOR_SAML_ACCOUNT_INVITES is enabled.
Continuous Integration
This release includes a new Docker delegate that you can install directly on a host. This feature is behind the Feature Flag CI_DOCKER_INFRASTRUCTURE. (CI-5680)
September 7, 2022
Harness Platform
You can now create a Harness Custom Secret Manager in Next Gen. (PL-25545)
You can onboard any secret manager with Harness and reference their secrets in Harness using a Shell Script.
This is behind the feature flag CUSTOM_SECRET_MANAGER_NG.
See Add a custom secret manager.
July 7, 2022
Harness Platform
Simplified Git Experience
Harness Git Experience lets you store configurations for your resources like Pipelines, Input Sets in Git. You can choose Git as the source of truth and use your Git credentials to access and modify your configurations.
With Harness Git Experience, you can select the repository and branch from where you want to execute your Pipelines, hence simplifying your Pipeline execution by seamless access to your Harness resources and their configurations stored in Git.
For more information, refer to Harness Git Experience Overview.
This functionality is behind a feature flag: NG_GIT_EXPERIENCE